Archive
Virtualization Career Training
Microsoft Technical Evangelists Symon Perriman and Rick Claus are hosting an online conference on Virtualization Career Training with Microsoft Learning
Virtualization Career Training
On Tuesday, October 4th Technical Evangelists Symon Perriman and Rick Claus are hosting an online conference on Virtualization Career Training with Microsoft Learning. This half day virtual event (8am – 11am PST) will offer a Level100to 200 introduction for anyone who wants to learn more about Microsoft Virtualization and how it can help their career. It is free and public so sign up for this warm-up for the Jump Start event on October 6th.
·Module 1 – Technology: Learn about Microsoft’s virtualization technologies, how they work, and the future roadmap to the Cloud!
·Module 2 – Career: Understand the importance of virtualization and Private Cloud, and how it can make or break an IT Professional’s career!
·Module 3 – Certification: Get prepared for your next steps towards a virtualization career by understanding and preparing for the Microsoft 70-659 Technical Specialist exam,Windows Server 2008 R2, Server Virtualization.
Learn More: http://mctreadiness.com/MicrosoftCareerConferenceRegistration.aspx?pid=270
Register: http://mctreadiness.com/MicrosoftCareerConferenceRegistration.aspx?pid=288
Instructor Bios: http://mctreadiness.com/MicrosoftCareerConferenceRegistration.aspx?pid=287

Virtualization Exam 70-659 Training
On Thursday October 6th Technical Evangelist Symon Perriman and Technical Instructor Philip Helsel will host an online 8-hour deep dive training event forthe Microsoft 70-659 Technical Specialist exam, Windows Server 2008 R2, Server Virtualization. This virtual event runs from 8am to 5pm PST and will include presentations, demos and live Q&A with the attendees. It costs $99 to attend, but includes a free exam voucher worth $150! It is public so sign up for some great training to help improve your career here:http://mctreadiness.com/MicrosoftCareerConferenceRegistration.aspx?pid=272. Register early to make the most of a weekly virtualization coaching newsletter!
·Module 1 – Installing and Configuring Host and Parent Settings
·Module 2 – Configuring Child Settings
·Module 3 – Managing and Monitoring Virtual Environments
·Module 4 – Ensuring High Availability and Recoverability
·Module 5 – Performing Migration
·Module 6 – Configuring Remote Desktop (RD) Role Services Infrastructure
Technologies that we will cover include: Windows Server 2008 R2, Hyper-V, System Center Virtual Machine Manager (VMM), System Center Operations Manager (OpsMgr), System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM), Windows Server Backup, Failover Clustering, Remote Desktop Services, Active Directory, Microsoft Assessment & Planning Toolkit (MAP), Virtual Machine Servicing Tool (VMST), Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) & more!
Learn More: http://mctreadiness.com/MicrosoftCareerConferenceRegistration.aspx?pid=274
Register: http://mctreadiness.com/MicrosoftCareerConferenceRegistration.aspx?pid=272
Exam Information: http://www.microsoft.com/learning/en/us/Exam.aspx?ID=70-659
Thanks!
Microsoft
Windows 8 Server : native support for NIC Teaming
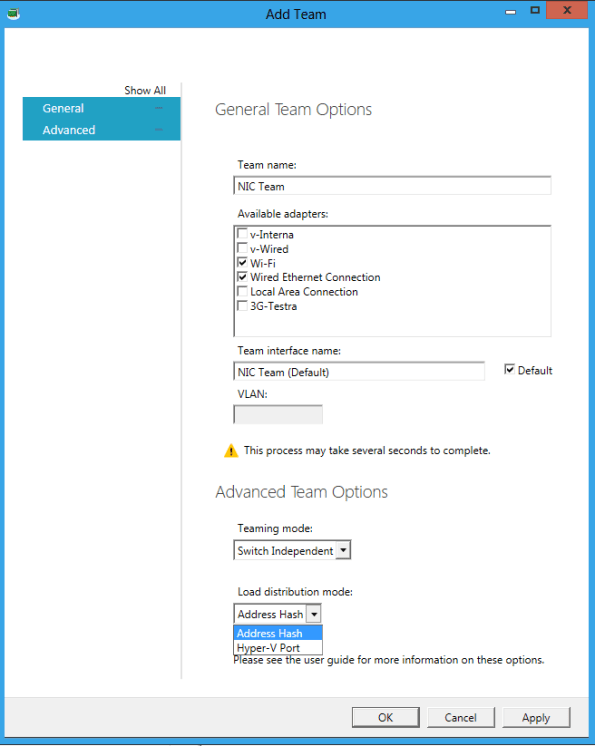
Windows 8 will come with native NIC Teaming, which means that we don’t need to pre-install or configure any software provided by the NIC vendor for the NIC TEAMING work.
Now you can team 2 or more NIC’s even if they are from different vendors configured as NIC Teaming and better, you can expose that NIC to Hyper-V Virtual Machines. This is really cool and one of the most wanted features.
The scenarios for application of the feature in production are infinite now, especially In High Availability environments. But please be aware that is the preview version! Much more still to come!
As an example, I installed Windows 8 with the NIC teaming configured using the Wireless NIC and the Wired NIC, then I went to the Hyper-V Manager and I created an Virtual Switch pointing to the NIC Team. How cool is that?
System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2012. What’s new in the RC version?
Microsoft is about to launch the SCVMM 2012 for those who tried the beta version and as myself enjoyed, we will now be able to try also the Release Candidate version.
To download : http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/gg678609
My recommendation to managege for up to 150hosts:
2 Processor, Dual-Core, 4GB Ram ( minumum ), 40 GB free space. Remember SCVMM 2012 requires Standard,Entrepise or Datacenter version of SQL Server ( you CAN’T use SQL express anymore ) and you must use a case-insensitive instance of SQL Server
As with the previous release there are a number of improved features for you to take advantage of. With this release you will be able to do:
- Setup Upgrade
- *New in RC -Upgrade- Setup will support the following upgrade paths
- VMM 2008 R2 SP1 > VMM for System Center 2012 RC > VMM for System Center 2012 RTM
- VMM for System Center 2012 RC > VMM for System Center 2012 RTM
- *New in RC -Upgrade- Setup will support the following upgrade paths
- Fabric Management
- Hyper-V and Cluster Lifecycle Management – Deploy Hyper-V to bare metal server, create Hyper-V clusters, orchestrate patching of a Hyper-V Cluster
- *New in RC:
- ISO or CD-based OSD for environments with DHCP without WDS
- OSD will now convert dynamic to fixed type of VHD destination
- All network adapters on host can be configured during provisioning
- *New in RC:
- Ability to bypass cluster validation during cluster creation
- Run cluster validation reports on-demand
- New cluster status tab to view an aggregated status, plus the cluster validation report
- Ability to see current CSV owner in the properties of the cluster
- *New in RC:
- Third Party Virtualization Platforms – Add and Manage Citrix XenServer and VMware ESX Hosts and Clusters
- Network Management – Manage IP Address Pools, MAC Address Pools and Load Balancers
- *New in RC:
- Simplification of the logical networks in the Fabric workspace
- Ability to see IP addresses that are in use from a IP pool
- Added support for Microsoft Network Load Balancer
- Gateway and DNS are no longer mandatory fields for logical networks
- Load balancer can now support affinity to logical networks
- *New in RC:
- Storage Management – Classify Storage, Manage Storage Pools and LUNs
- *New in RC
- Create persistent sessions to iSCSI array and logon initiator to array
- Better scalability of storage operations – LUN create, snapshot, clone, masking, and unmasking
- Option to create storage groups per cluster (BETA only supported creation of storage group per node in a cluster)
- Enablement of MPIO feature when provisioning a new Hyper-V server
- Automatic MPIO device claim
- Support for arrays that implement OnePortPerView
- *New in RC
- Update Management- Keep your SCVMM Fabric Servers (SCVMM roles, hosts, and clusters) up-to-date with patches.
- *New in RC:
- Share a WSUS root server between System Center Configuration Manager 2007 R2/ System Center Configuration Manager 2012 Beta
- Hyper-V Cluster Orchestration- Nodes put into VMM Maintenance Mode can be set to trigger Maintenance Mode in Operations Manager.
- *New in RC:
- Hyper-V and Cluster Lifecycle Management – Deploy Hyper-V to bare metal server, create Hyper-V clusters, orchestrate patching of a Hyper-V Cluster
- Resource Optimization
- Dynamic Optimization – proactively balance the load of VMs across a cluster
- Power Optimization – schedule power savings to use the right number of hosts to run your workloads – power the rest off until they are needed.
- *New in RC:
- Set Operations Manager Mode for powered down hosts
- *New in RC:
- PRO – integrate with System Center Operations Manager to respond to application-level performance monitors.
- *New in RC:
- Support added for System Center Operations Manager 2012 Beta
- VMM will ship two sample PRO Packs: Cluster scale out and Service scale out MPs
- *New in RC:
- Cloud Management
- Abstract server, network and storage resources into private clouds
- Delegate access to private clouds with control of capacity, capabilities and user quotas
- Enable self-service usage for application administrator to author, deploy, manage and decommission applications in the private cloud
- Service Lifecycle Management
- Define service templates to create sets of connected virtual machines, OS images and application packages
- *New in RC:
- Service Designer and Specialization UI enhancements
- Added ability to use Service Template Patterns
- *New in RC:
- Compose operating system images and applications during service deployment
- *New in RC:
- IP-based provisioning
- New application instance view
- *New in RC:
- Scale out the number of virtual machines in a service
- Service performance and health monitoring integrated with System Center Operations Manager
- Decouple OS image and application updates through image-based servicing
- *New in RC:
- Streamlined ability to enable OS VHD updates to a Service Template
- Publish updated Service Templates in order to update Service Instances
- *New in RC:
- Leverage powerful application virtualization technologies such as Server App-V
- Define service templates to create sets of connected virtual machines, OS images and application packages
I hope you enjoy as much as I enjoyed!
Post comments about your SCVMM 2012 experience!
Windows 8 : Hyper-V’s “Live Storage Move”
Hyper-V’s “Live Storage Move” capability helps your VMs to be fairly independent of the underlying storage. With this, you could move the VM’s storage from one local drive to another, to a USB stick, or to a remote file share without needing to stop your VM.
This feature is helpfull for fast deployments, when for you need example a VM quickly, you can then start one from a VM library maintained on a file share and then move the VM’s storage to another local drive.
Other good example will be when the physical disk is full. You will then quickly be able to move the VM’s storage to other drive.
For storage, you can add multiple hard disks to the IDE or SCSI controllers available in the VM. You can use Virtual Hard Disks (.VHD or .VHDX files) or actual disks that you pass directly through to the virtual machine. VHDs can also reside on a remote file server, making it easy to maintain and share a common set of predefined VHDs across a team.
More info: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2011/09/07/bringing-hyper-v-to-windows-8.aspx
Windows 8 Desktop Client version will have Hyper-v x64-bit VM’s
Microsoft announced that the upcoming Windows 8 desktop version will have Hyper-v which will support x64-bit VM’s
Hyper-V requires a 64-bit system that has Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). SLAT is a feature present in the current generation of 64-bit processors by Intel & AMD.
You’ll also need a 64-bit version of Windows 8, and at least 4GB of RAM. Hyper-V does support creation of both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems in the VMs.
Plus, Hyper-V’s dynamic memory allows memory needed by the VM to be allocated and de-allocated dynamically (you specify a minimum and maximum) and share unused memory between VMs.
As for user experience with VMs, Windows provides two mechanisms to peek into the Virtual Machine: the VM Console and the Remote Desktop Connection.
The VM Console (also known as VMConnect) is a console view of the VM. It provides a single monitor view of the VM with resolution up to 1600×1200 in 32-bit color. This console provides you with the ability to view the VM’s booting process.
Features or applications that depend on specific hardware will not work well in a VM. For example, Windows BitLocker, Measured Boot, games or applications that require processing with GPUs, also, applications relying on sub 10ms timers, i.e. latency-sensitive high-precision apps such as live music mixing apps, etc. could have issues running in a VM.
The root OS is also running on top of the Hyper-V virtualization layer, but it is special in that it has direct access to all the hardware. This is why applications with special hardware requirements continue to work unhindered in the root OS but latency-sensitive, high-precision apps could still have issues running in the root OS.
SCVMM 2012 Storage and Load Balancer Provider downloads
In SCVMM 2012, in
order to have Storage and Load Balance integration you will need the Provider.
For the Storage you
will need the SMI-S provider and for the Load Balance you will need their
custom provider.
If you are looking for
the download links for the SCVMM 2012 Storage and Load Balance Providers, here
is the list:
| Type | Manufacturer | Version | Link/Instructions | Additional Information |
| Load Balancer | F5 | 3.0.0.175 | Click here | Registration required |
| Citrix | 0.9.0 | Click here | ||
| SMI-S Provider | NetApp | 4.0 X2 | Click here | Registration required |
| EMC | 4.2.1 | Click here | Registration required |
|
| HP | 9.3 | Built-in to HP StorageWorks CommandViewEVA |
Requires SMI-S CIMOM to enabled |
|
| Dell | Click here for MD32x0/i and MD36x0/i Storage Array |
Registration required |
Storage : SMI-S Provider tested for vs.1.4
| Vendor |
| Brocade |
| Dell |
| EMC Corporation |
| Hewlett-Packard |
| Hitachi |
| Huawei Symantec |
| IBM |
| LSI, Engenio Storage Group |
| PMC-Sierra |
Source : http://www.snia.org/ctp/
Windows 8 : Windows Explorer gets new interface : now with ribbon ( office 2010 like )
Windows 8 is comming with lot of good surpises. I just heard about the new ribbon:
The new ribbon
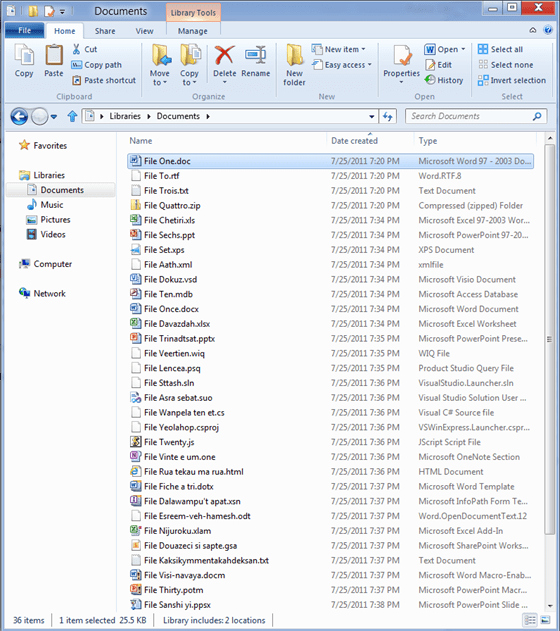
The Home tab is focused on the core file management tasks, and we’ve put all the major file management commands there in prominent locations: Copy, Paste, Delete, Rename, Cut, and Properties. We’ve also given new prominence to two popular heritage features, Move to and Copy to, along with exposing a hidden gem, Copy path, which is really useful when you need to paste a file path into a file dialog, or when you want to email someone a link to a file on a server.
The Home tab is the heart of our new, much more streamlined Explorer experience. The commands that make up 84% of what customers do in Explorer are now all available on this one tab:

Overlay showing Command usage % by button on the new Home tab
The Share tab is for sharing files by typical methods like zipping them up and emailing them to a friend, or burning them to optical media. Or you can quickly share files with other people in your home group or your network domain. It also provides one-click access to the ACLs for the currently highlighted file.
Source : http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2011/08/29/improvements-in-windows-explorer.aspx
SCVMM 2012 : Ports commnications for Firewall Configuration
When you install the SCVMM 2012 you can assign some of the ports that it will use for communications and file transfers between the VMM components.
Note: Not all of the ports can be changed through VMM.
The default settings for the ports are listed in the following table:
| Connection type | Protocol | Default port | Where to change port setting |
| SFTP file transfer from VMware ESX Server 3.0 and VMware ESX Server 3.5 hosts | SFTP | 22 | |
| VMM management server to P2V source agent (control channel) | DCOM | 135 | |
| VMM management server to Load Balancer | HTTP/HTTPS | 80/443 | Load balancer configuration provider |
| VMM management server to WSUS server (data channel) | HTTP/HTTPS | 80/8530 (non-SSL), 443/8531 (with SSL) |
These ports are the IIS port binding with WSUS. They cannot be changed from VMM. |
| VMM management server to WSUS server (control channel) | HTTP/HTTPS | 80/8530 (non-SSL), 443/8531 (with SSL) | These ports are the IIS port binding with WSUS. They cannot be changed from VMM. |
| BITS port for VMM transfers (data channel) | BITS | 443 | During VMM setup |
| VMM library server to hosts file transfer | BITS | 443 (Maximum value: 32768) | During VMM setup |
| VMM host-to-host file transfer | BITS | 443 (Maximum value: 32768) |
|
| VMM Self-Service Portal to VMM Self-Service Portal web server | HTTPS | 443 | During VMM setup |
| VMware Web Services communication | HTTPS | 443 | VMM console |
| SFTP file transfer from VMM management server to VMware ESX Server 3i hosts | HTTPS | 443 | |
| OOB Connection – SMASH over WS-Man | HTTPS | 443 | On BMC |
| VMM management server to in-guest agent (VMM to virtual machine data channel) | HTTPS (using BITS) |
443 | |
| VMM management server to VMM agent on Windows Server–based host (data channel for file transfers) | HTTPS (using BITS) |
443 (Maximum value: 32768) |
|
| OOB Connection IPMI | IPMI | 623 | On BMC |
| VMM management server to remote Microsoft SQL Server database | TDS | 1433 | |
| Console connections (RDP) to virtual machines through Hyper-V hosts (VMConnect) | RDP | 2179 | VMM console |
| VMM management server to Citrix XenServer host (customization data channel) | iSCSI | 3260 | On XenServer in transfer VM |
| Remote Desktop to virtual machines | RDP | 3389 | On the virtual machine |
| VMM management server to VMM agent on Windows Server–based host (control channel) | WS-Management | 5985 | During VMM setup |
| VMM management server to in-guest agent (VMM to virtual machine control channel) | WS-Management | 5985 | |
| VMM management server to VMM agent on Windows Server–based host (control channel – SSL) | WS-Management | 5986 | |
| VMM management server to XenServer host (control channel) | HTTPS | 5989 | On XenServer host in: /opt/cimserver/cimserver_planned.conf |
| VMM console to VMM management server | WCF | 8100 | During VMM setup |
| VMM Self-Service Portal web server to VMM management server | WCF | 8100 | During VMM setup |
| VMM console to VMM management server (HTTPS) | WCF | 8101 | During VMM setup |
| Windows PE agent to VMM management server (control channel) | WCF | 8101 | During VMM setup |
| VMM console to VMM management server (NET.TCP) | WCF | 8102 | During VMM setup |
| WDS provider to VMM management server | WCF | 8102 | During VMM setup |
| VMM console to VMM management server (HTTP) | WCF | 8103 | During VMM setup |
| Windows PE agent to VMM management server (time sync) | WCF | 8103 | During VMM setup |
| VMM management server to Storage Management Service | WMI | Local call |
|
| VMM management server to Cluster PowerShell interface | PowerShell | n/a | |
| Storage Management Service to SMI-S Provider | CIM-XML | Provider-specific port |
|
| VMM management server to P2V source agent (data channel) | BITS | User-Defined | P2V cmdlet option |
SCOM 2007 R2 : Monitoring Pack for Windows Azure
The Windows Azure Monitoring Management Pack enables you to monitor the availability and performance of applications that are running on Windows Azure.
After configuration, the Windows Azure Monitoring Management Pack offers the following functionality:
- Discovers Windows Azure applications.
- Provides status of each role instance.
- Collects and monitors performance information.
- Collects and monitors Windows events.
- Collects and monitors the .NET Framework trace messages from each role
instance. - Grooms performance, event, and the .NET Framework trace data from Windows
Azure storage account. - Changes the number of role instances via a task
System Center Monitor version : System Center Operations Manager 2007 R2 CU3 or newer
More detalis : http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=11324
Hyper-v: Detailed step by step installing RedHat 6.1 VM in expert mode with the new Linux Integration Services 3.1
Microsoft released the a new Linux Integration Services, fully tested against RHEL 6.0, RHEL 6.1, and CentOS 6.0
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=26837
To Create a RedHat 6 VM
1. Open Hyper-V Manager: Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click
Hyper-V Manager.
2. Create a new virtual machine where you will install Linux: In the Actions menu, click New, and then click Virtual Machine.
Note: if you do not Add a legacy network adapter a this point, the virtual machine will not have network support, until you install the Linux Integration Services.
3. Specify the Linux installation media: Right-click the virtual machine that you created, and then click Settings. In IDE Controller, specify one of the following:
a. An image file in ISO format that contains the files required for installation
b. A physical CD/DVD drive that contains the installation media
4. Turn on the virtual machine: Right-click the virtual machine that you created, and then click Connect.
To Install Redhat Linux 6.1
1. After a short delay, the Welcome to Red Hat Linux 6.1! screen appears. Press <Tab>
2.At the prompt, add the text: append expert and then press <Enter>
3. Press <OK> to check the installation media or <SKIP> to not test check in the next screen
4. Click Next to continue
5. The Choose a Language screen appears. This screen asks you to select the language to be used during the installation process. Use the up-or down-arrow key to select alanguage (the system highlights your choice). Click Next
6.The Keyboard Type screen appears asking you to select a keyboard type. Use the up- or down-arrow key to select a keyboard type (the system highlights your choice). Click Next
7. At the “Devices” screen select Basic Storage Devices to install Red Hat Enterprise Linux on the following storage devices: hard drives or solid-state drives connected directly to the local system
8. As you selected Basic Storage Devices, anaconda automatically detects the local storage attached to the system and does not require further input.Click Next.
9. Enter the Hostname for your server, select OK
10 If you added the Legacy Network at the creation of the VM, then click Configure Network . At the “Network Configuration” window, Specify an IP address/gateway. Otherwise, skip this task. You can setup the network later, after installing the Linux Integration Services

Use the IPv4 Settings tab to configure the IPv4 parameters for the previously selected network connection. Select Start automatically to start the connection automatically when the system boots.
11.Click Next
12. At the “Time Zone Selection” window, highlight the correct time zone. Click Next
13.For Root Password, type and confirm the password. Click Next
14. If no readable partition tables are found on existing hard disks, the installation program asks to initialize the hard disk. This operation makes any existing data on the hard disk unreadable. If your system has a brand new hard disk with no operating system installed, or you have removed all partitions on the hard disk, click Re-initialize drive
15. Select the type of installation would you like and then click Next.
Note: If you chose one of the automatic partitioning options (first 4 options) and selected Review, you can either accept the current partition settings (click Next), or modify the setup manually in the partitioning screen. To review and make any necessary changes to the partitions created by automatic partitioning, select the Review option. After selecting Review and clicking Next to move forward, the partitions created for you by anaconda appear. You can make modifications to these partitions if they do not meet your needs.
If you chose to create a custom layout, you must tell the installation program where to install Red Hat Enterprise Linux. This is done by defining mount points for one or more disk partitions in which Red Hat Enterprise Linux is installed. You may also need to create and/or delete partitions at this time
Unless you have a reason for doing otherwise, I recommend that you create the following partitions for x86, AMD64, and Intel
64 systems:
• swap partition
• /boot partition
• / partition
Advice on Partitions:
- A swap partition (at least 256 MB) — swap partitions are used to support virtual memory. In other words, data is written to a swap partition when there is not enough RAM to store the data your system is processing. In years past, the recommended amount of swap space increased linearly with the amount of RAM in the system. But because the amount of memory in modern systems has increased into the hundreds of gigabytes, it is now recognized that the amount of swap space that a system needs is a function of the memory workload running on that system. However, given that swap space is usually designated at install time, and that it can be difficult to determine beforehand the memory workload of a system, use the recommended:
| Amount of RAM in the System | Recommended Amount of Swap Space |
| 4GB of RAM or less | a minimum of 2GB of swap space |
| 4GB to 16GB of RAM | a minimum of 4GB of swap space |
| 16GB to 64GB of RAM | a minimum of 8GB of swap space |
| 64GB to 256GB of RAM | a minimum of 16GB of swap space |
- The /var directory holds content for a number of applications. It also is used to store downloaded update packages on a temporary basis. Ensure that the partition containing the /var directory has enough space to download pending updates and hold your other content.
- The /usr directory holds the majority of software content on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system. For an installation of the default set of software, allocate at least 4 GB of space.
If you are a software developer or plan to use your Red Hat Enterprise Linux system to learn software development skills, you may want to at least double this allocation. - Consider leaving a portion of the space in an LVM volume group unallocated. This unallocated space gives you flexibility if your space requirements change but you do not wish to remove data from other partitions to reallocate storage
16. After finishing creating the partitions, Click Next. The installer prompts you to confirm the partitioning options that you selected. Click Write changes to disk to allow the installer to partition your hard drive and install Red Hat Enterprise Linux
17.Allow the installation process to complete. The Package Installation Defaults screen appears and details the default package set for the Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation
If you select Basic Server, this option will provide a basic installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux for use on a server.
18. Select Customize now to specify the software packages for your final system in more detail. This option causes the installation process to display an additional customization screen when you select Next. The following screens shows the customized packages selected

Note : The packages that you select are not permanent. After you boot your system, use the Add/Remove Software tool to either install new
software or remove installed packages. To run this tool, from the main menu, select System -> Administration -> Add/Remove Software
19. Click Next to continue the installation. The installer checks your selection, and automatically adds any extra packages required to use the software you selected. The installation process will start. At this point there is nothing left for you to do until all the packages have been installed.
20. Installation Complete: Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation is now complete. select Reboot to restart your Virtual Machine

Now it’s time for the first-boot configuration.
21. First Boot lets you configure your environment at the beginning. Click Forward to proceed
22. Accept the License and Click Forward to proceed
23. Setting up software updates. Select whether to register the system immediately with Red Hat Network. To register the system, select Yes, I’d like to register now, and click Forward.
Note : it can be registered with the RedHat Entitlement Service later using the Red Hat Subscription Manager tools
24. Create User to use as a regular non-administrative use. Enter a user name and your full name, and then enter your chosen password. Type your password once more in the Confirm Password box to ensure that it is correct.
Note: If you do not create at least one user account in this step, you will not be able to log in to the RedHat Enterprise Linux graphical environment
25. Click Forward to proceed
26. Date and Time. Use this screen to adjust the date and time of the system clock.
27. Click Forward to proceed
28. Kdump. Use this screen to select whether or not to use the Kdump kernel crash dumping mechanism on this system. Note that if you
select this option, you will need to reserve memory for Kdump and that this memory will not be available for any other purpose.
29 Click Finish to proceed.
Done installation and configuration of RedHat Linux 6.1 completed. Not let’s configure the Linux Integration Services.
To install Linux Integration Services Version 3.1
Important Note: There is an issue where the SCVMM 2008 Service can crash with VMs running Linux Integration Components v3.1 for Hyper-V.
Resolution: Disabling the KVP daemon on the Linux virtual machine will prevent the SCVMM service crash. The command to make this change must be run as root.#/sbin/chkconfig –level 35 hv_kvp_daemon off
This will prevent the KVP service from auto starting while retaining all other functionality of hv_utils. hv_utils provides integrated shutdown, key value pair data exchange, and heartbeat features. More info : http://blogs.technet.com/b/scvmm/archive/2011/07/28/new-kb-the-scvmm-2008-virtual-machine-manager-service-crashes-with-vms-running-linux-integration-components-v3-1-for-hyper-v.aspx
1. Log on to the virtual machine.
2. In Hyper-V Manager, configure LinuxIC v30.ISO (located in the directory where you extracted the downloaded files) as a physical CD/DVD drive on the virtual machine.

3. Open a Terminal Console ( command line )
4. As the root user, mount the CD in the virtual machine by issuing the following command at a shell prompt:
#mount /dev/cdrom /media

4. As the root user, run the following command to install the synthetic drivers. A reboot is required after installation.
For 64-bit versions:
# yum install /media/x86_64/kmod-microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.x86_64
# yum install /media/x86_64/microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.x86_64
# reboot
or if you prefer to use rpm:
# rpm –ivh /media/x86_64/kmod-microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.x86_64.rpm
# rpm –ivh /media/x86_64/microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.x86_64.rpm
# reboot
For 32-bit versions:
# yum install /media/x86/kmod-microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.i686
#yum install /media/x86/microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.i686
# reboot
or
# rpm –ivh /media/x86/kmod-microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.i686.rpm
# rpm –ivh /media/x86/microsoft-hyper-v-rhel6-60.1.i686.rpm
# reboot
DONE! You should now have RedHat 6.1 running as VM on Hyper-V.
Note:
After Linux Integration Services are installed on the virtual machine, Key Value Pair exchange functionality is activated. This allows the virtual machine to provide the following information to the virtualization server:
-
Fully Qualified Domain Name of the virtual machine
-
Version of the Linux Integration Services that are installed
-
IP Addresses (both IPv4 and IPv6) for all Ethernet adapters in the virtual machine
-
OS Build information, including the distribution and kernel version
-
Processor architecture (x86 or x86-64)
The data can be viewed using the Hyper-V WMI provider, and accessed via Windows PowerShell. Instructions for viewing Key Value Pair exchange data are available at these websites:
http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/hyper-v-script-to-check-icversion.aspx
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/virtual_pc_guy/archive/2008/11/18/hyper-v-script-looking-at-kvpguestintrinsicexchangeitems.aspx