Archive
Hyper-V Windows 2012 : High Availability and Resiliency : new enhancements
There are a number of new enhancements that ensure key workloads are resilient, and protected.
• Hyper-V Replica – Asynchronous, application-consistent virtual machine replication and it does not depend on any hardware vendor. You can establish an Hyper-V Replica between 2 separated physical locations without a storage. It permits asynchronous replication of Hyper-V virtual machines between two locations for business continuity and failure recovery.
• Incremental Backups – True differential disk backups of virtual hard disks to help ensure that the data is backed up and restored when necessary. It also reduces storage costs because it backs up only what has changed, not the entire disk.
• NIC Teaming – Provides increased reliability and performance for virtual machines and now does not depends on manufacturer drivers.
• Hyper-V Clustering Enhancements – Unmatched scale and flexibility for virtualized infrastructures:
• Unmatched Scale – Windows Server 2012 support up to 64 physical nodes and up to 4,000 virtual machines in a single cluster providing scalability and flexibility for key virtualized workloads.
• Flexible Virtual Machine Guest Clustering – Provides not only iSCSI guest clustering support, including MPIO, but also enables the use of Virtual Fibre Channel adapters within the virtual machine allowing workloads access to storage area networks using fiber channel fabric. In addition, a virtual fibre channel enables IT to cluster guest operating systems over Fibre Channel providing HA for workloads within VMs and utilize the built-in Windows multi-path I/O (MPIO) for high-availability and load balancing on the storage path. By employing MPIO and Failover Clustering together as complimentary technologies, users are able to mitigate the risk of a system outage at both the hardware and application levels.
• Highly Secure Clustered Storage – Hyper-V, Failover Clustering and BitLocker now work in concert to create the ideal and secure platform for private cloud infrastructure. Windows Server 2012 Cluster disks that are encrypted using BitLocker Drive Encryption enable better physical security for deployments outside secure data centers, providing a critical safeguard for the cloud and helping protect against inadvertent data leaks
• Enhanced Cluster Shared Volumes – Cluster Shared Volume 2.0 (CSV). CSV has been greatly enhanced in a number of ways. From a usability standpoint, CSV is now a core Failover Clustering feature, with simplified administration and management. To support up to 64 nodes in a cluster, CSV has been improved in aspects of both performance and scalability. In terms of integrating with our partners, CSV has specifically been enhanced to work out of the box with storage filter drivers such as those used by: anti-virus, data protection, backup and storage replication ensuring a more seamless integration with existing investments.
• 3 Levels of Availability – Bringing higher availability to workloads that do not support clustering. It does this by providing a light-weight, simple solution to monitor applications running in the VMs and integrating with the host. By monitoring services and event logs inside the virtual machine, Hyper-V and Failover Clustering can detect whether the key services that a virtual machine provides are healthy and provide automatic corrective action such as restarting the virtual machine or restarting a service within the VM. This is in addition to the already existing virtual machine failover capabilities should a host fail, or the virtual machine itself become unresponsive.
• Cluster-Aware Updating – An in-box end-to-end solution for updating Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V Failover Clusters, helping customers to preview, apply, and report on updates, all with zero downtime to the virtual machines.
• Virtual Machine Failover Prioritization – Virtual machine priorities can now be configured to control the order in which specific virtual machines failover or start. This ensures higher priority virtual machines are given the resources they need and lower priority virtual machines are given resources as they are available.
• Affinity (and Anti-Affinity) Virtual Machine Rules – Administrators can now configure partnered virtual machines so that at failover, the partnered machines are migrated simultaneously. For example, administrators can configure their SharePoint virtual machine and the partnered SQL Server virtual machine to always failover together to the same node. Administrators can also specify that two specific virtual machines cannot coexist on the same node in a failover scenario.
How Does VmWare compare?
| Capability | Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V |
VMware ESXi 5.0 |
VMware vSphere 5.0 Enterprise Plus |
| Incremental Backups |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
| VM Replication |
Yes |
No |
vCenter SRM |
| NIC Teaming |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Integrated High Availability |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
| Guest OS Application Monitoring |
Yes |
N/A |
No |
| Cluster-Aware Updating |
Yes |
N/A |
Yes |
| Failover Prioritization |
Yes |
N/A |
Yes |
| Affinity & Anti-Affinity Rules |
Yes |
N/A |
Yes |
What are you waiting for? start today your own POC of Windows 2012 !
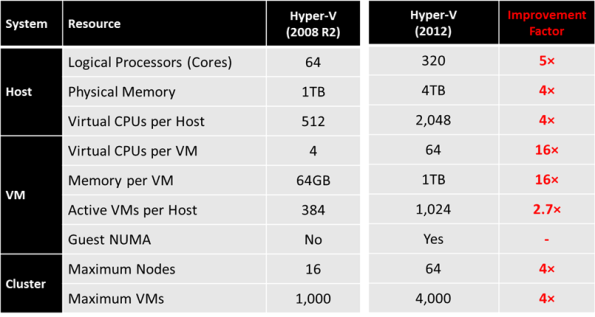
Hyper-V Windows 20012 improvments and comparison
Significant improvements have been made across the board, with Hyper-V now supporting increased cluster sizes, a significantly higher number of active virtual machines per host, and additionally, more advanced performance features such as in-guest Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA).
The tables below shows the improvement Microsoft has done with Windows 20012 Hyper-V :
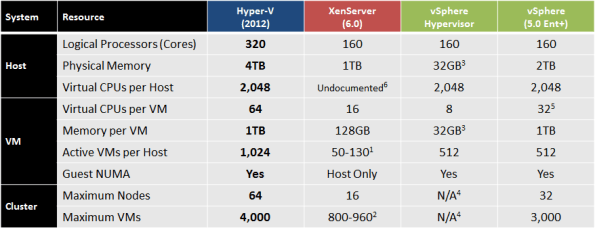
The table also shows that both Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V and vSphere 5.0 Enterprise Plus deliver up to 1TB of memory to an individual virtual machine, however, one aspect to bear in mind when creating virtual machines of this size, is the vRAM (Virtual Machine Memory) entitlement with vSphere 5.0.
- Each vSphere 5.0 Enterprise Plus CPU license comes with a vRAM entitlement of 96GB vRAM, and on a 2 CPU physical host, this would equate to 192GB vRAM added to a ‘vRAM Pool’
- The 1TB virtual machine would consume 96GB of the vRAM allocation (this is an upper limit established for an individual VM, and was one of the results of customer feedback around the original vRAM licensing announcements)
- This would leave only 96GB of vRAM for use by other virtual machines, restricting scale. The only option to overcome this would be for the customer to purchase additional vSphere 5.0 licenses at considerable expense. This is on top of the extra administrative overhead of monitoring and managing vRAM entitlements.
Notes:
Solutions for Private, Public, and Hybrid Clouds and Introducing Windows Server 2012 : Free e-books
Introducing Windows Server 2012
If you are looking for an early, high-level view of Windows Server 2012, this guide introduces its new features and capabilities, with scenario-based insights demonstrating how the platform can meet the needs of your business. Click here to download.
Solutions for Private, Public, and Hybrid Clouds
Make sure to read chapter one for information on why cloud computing is the most efficient and cost-effective way to deliver computing resources to users according to your business needs:
Chapter 1: Microsoft Solutions for Private, Public and Hybrid Clouds. Click here.
Chapter 2: From Virtualization to the Private Cloud – Click here
Chapter 3: Public and Hybrid Clouds. Click here
SYSRET 64-bit OS privilege vulnerability on Intel, DOES NOT AFFECT HYPER-V
Last week US-CERT warned of guest-to-host VM escape vulnerability and it was reported that an issue on Intel based servers could lead to a “break out” from a VM to the host in certain virtualisation products, including Microsoft : “A ring3 attacker may be able to specifically craft a stack frame to be executed by ring0 (kernel) after a general protection exception (#GP). The fault will be handled before the stack switch, which means the exception handler will be run at ring0 with an attacker’s chosen RSP causing a privilege escalation” : http://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/649219
Affected vendors include Intel Corp., FreeBSD, Microsoft, NetBSD, Oracle, RedHat, SUSE Linux and Xen.
But Hyper-V is NOT Affected By VU#649219 VM “Break Out”.
I’ve asked the Microsoft Hyper-V product team Redmond if Hyper-V was actually affected and as per their answer:
•The problem does affect the 64-bit OS’s on Intel hardware, but Hyper-V is not affected.
•This problem will not lead to break outs from Hyper-V VMs.
•Windows 8 is not affected
•Windows Server 2012 is not affected.
This was covered as well by Aidan Finn : http://www.aidanfinn.com/?p=12838
Hyper-V Windows 2012: Enhanced Storage Capabilities. How does VMware compare
Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V introduces a number of enhanced storage capabilities to support the most intensive, mission-critical of workloads:
• Virtual Fiber Channel – Enables virtual machines to integrate directly into Fiber Channel Storage Area Networks (SAN), unlocking scenarios such as fiber channel-based Hyper-V Guest Clusters.
•Support for 4-KB Disk Sectors in Hyper-V Virtual Disks. Support for 4,000-byte (4-KB) disk sectors lets customers take advantage of the emerging innovation in storage hardware that provides increased capacity and reliability.
•New Virtual Hard Disk Format. This new format, called VHDX, is designed to better handle current and future workloads and addresses the technological demands of an enterprise’s evolving needs by increasing storage capacity, protecting data, improving quality performance on 4-KB disks, and providing additional operation-enhancing features. The maximum size of a VHDX file is 64TB.
•Offloaded Data Transfer (ODX). With data transfer support, the Hyper-V host CPU can concentrate on the processing needs of the application and offload storage-related tasks to the SAN, increasing performance.
Hyper-V provides a number of advantages over VmWare, with Hyper-V providing highest levels of availability and performance. Hyper-V also gives you the ability to utilize Device Specific Modules, also known as DSMs, produced by storage vendors, in conjunction with the Multipath I/O framework within Windows Server, ensures that customers run their workloads on an optimized configuration from the start, as the storage vendor intended, providing the highest levels of performance and availability. (Note: Only the Enterprise and Enterprise Plus editions of vSphere 5.0, through a feature known as ‘vStorage APIs for Multipathing’, provide this capability, meaning customers have to upgrade to higher, more costly editions in order to unlock the best performance from their storage investments.)
Also, by integrating Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V with an ODX-capable storage array, many of the storage-related tasks that would normally use valuable CPU and network resources on the Hyper-V hosts, are offloaded to the array itself, executing much faster, increasing performance significantly, and unlocking extra resources on the hosts themselves.
How does VMware compare?
| Capability | Windows Server 2012 RC Hyper-V | VMware ESXi 5.0 | VMware vSphere 5.0 Enterprise Plus |
| Virtual Fiber Channel | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3rd Party Multipathing (MPIO) | Yes | No | Yes (VAMP) |
| Native 4-KB Disk Support | Yes | No | No |
| Maximum Virtual Disk Size | 64TB VHDX | 2TB VMDK | 2TB VMDK |
| Maximum Pass Through Disk Size | Varies | 64TB | 64TB |
| Offloaded Data Transfer | Yes | No | Yes (VAAI) |
System Center VMM 2012 SP1 CTP2: What’s new
Microsoft announced the availability of CTP2 of System Center 2012 SP1.
With support for Windows 2012 and SQL 2012 introduced in CTP1, here are what’s more :
. Network Virtualization: Introduced in CTP1, this release adds support for using DHCP to assign customer addresses and for using either the IP rewrite or IP encapsulation mechanism to virtualize the IP address of a virtual machine.
· VHDX support: Introduced in CTP1, you can now convert from .vhd to .vhdx. In addition, placement determines the format of a VHD based on the OS of the destination host (when you create a virtual machine with a blank virtual hard disk), and the provisioning of a physical computer as a Hyper-V host supports the use of a .vhdx file as the base operating system image.
· Storage Enhancements: Support for the new Windows Standards-Based Storage Management service, which enables you to discover storage by using multiple provider types. In addition, this release adds support for the thin provisioning of logical units, and for the discovery of Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) storage.
· Provisioning a Hyper-V Host Enhancements: Support for performing deep discovery to retrieve detailed information about physical network adapters.
· Support for VMM Console Add-Ins: You can now create Add-Ins and extend the VMM console. Add-Ins allow you to enable new actions or additional configuration for VMM objects by writing an application that uses context passed about the selected VMM objects. You can also embed custom WPF UI or web portals directly into the console’s main views to provide a more fully-integrated experience.
In App Controller, you can deploy and manage in a single console, applications running in Windows Azure PaaS, IaaS, on premises VMM clouds, and clouds provided by hosting providers. In addition, there are the following new features:
· Windows Azure Virtual Machine support: In addition to supporting Windows Azure PaaS workloads, App Controller adds support to the newly announced IaaS virtual machines in CTP2. You can easily deploy, manage, and operate Windows Azure Virtual Machines.
· Copy VMs from private cloud to public cloud: In CTP2, you can select a VMM private cloud VM and copy it to Windows Azure. App Controller makes upload disk, convert settings, and deploying a new virtual machine into an easy migrate flow!
· Hosting Provider support: In addition to on premises VMM private cloud and Windows Azure public cloud, App Controller supports connecting to VMM clouds at a hosting provider. You can connect to a hosting provider and manage user access to these clouds. You can also deploy, manage, and operate virtual machines at the hosting provider.
Also, check the the Project code-named “Service Provider Foundation” for System Center 2012 Service Pack 1 (SP1) provides a rich set of web services that manages Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) for System Center 2012 SP1. The infrastructure of Virtual Machine Manager is exposed through “Service Provider Foundation” as a web service. Because of this, you can manage this System Center component through the web services; for example, you can create or delete virtual machines.
“Service Provider Foundation” provides a web service that acts as an intermediary between web-based administration client and server applications. The web service supports REST-based requests using the OData protocol. The web service handles these requests through Windows PowerShell scripts to communicate and manage server applications.
High Availabilty. Why Hyper-V delivers better
That’s kind of interesting subject to talk about
Taking as a sample 3 cluster node, where every node has 1(one) connection to a shared storage.
By using VmWare, if one of the VmWare hosts ever lose the IP storage connectivity ( an fault on the ISCSI nic for example ), your Virtual Machines are on the dark, you will probably receive an Blue Screen. The VmWare monitoring will try to start (vmotion) the Virtual machine on the same host or on any other host that has storage connectivity.
Now, the clever solution from the Hyper-V
if the one of the Hyper-V hosts lose IP storage connectivity ( an fault on the ISCSI nic for example ), the Hyper-V will redirect the Storage traffic to the CSV and the VM still working : no blue screen, no restart.
In a Hyper-V Failover Cluster with CSV, all storage I/O is Direct I/O meaning each node hosting a virtual machine(s) is writing directly (via Fibre Channel, iSCSI, or SAS connectivity) to the CSV volume. But in case of lost of Storage connectivity in one of the hosts the traffic will be redirected over the CSV network to another node Host in the cluster which still has direct access to the storage supporting the CSV volume. This functionality prevents the loss of all connectivity to storage. Instead, all storage related I/O is redirected over the CSV network. This is very powerful technology as it prevents a total loss of connectivity thereby allowing virtual machine workloads to continue functioning.
Of course there are other fault scenarios to consider and yes, I know that the recommedation is to have redundant storage connection, but that’s kind of expensive solution and does not take the fact that the Hyper-V solution is more clever.
If you ever experienced this situation I would like to hear your input.
Windows Server 2012: Hyper-V Network Virtualization
Hyper-V Network Virtualization allow customers to keep their own internal IP addresses when moving to the cloud while providing isolation from other customers’ VMs – even if those VMs happen to use the exact same IP addresses.
The way it works is that each VM receive two IP addresses :
The first one, the IP address visible in the VM, is relevant in the context of a given tenant’s virtual subnet. Following the IEEE nomenclature we call this the Customer Address (CA).
The other IP address is relevant in the context of the physical network in the cloud datacenter. This is called the Provider Address (PA). This decoupling of tenant and datacenter IP addresses provides many benefits.
One of the benefits is that you can move your VMs to the cloud without modifying the VM’s network configuration and without worrying about what else (or who else) is sitting in that datacentre.
Another big reason is the policy enforcement in the end hosts that provides a scalable solution for multi-tenant isolation, instead of using Vlan’s, for isolation.
There are 2 different mechanisms to virtualize the IP address:
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) : should be used for network virtualization, because it provides the most flexibility and performance. It will be used for most environments/deployments
IP Rewrite : may be appropriate to provide performance and compatibility in some current high-capacity datacenters.
A very good article was posted by Jeffrey about this topic
Virtualizing ALL Domain Controllers in a Cluster environment. Would you recommend?
Would I recommend virtualizing All domain controllers on a Hyper-V Cluster?
My answer is : yes and NO.
1. Yes, for an home/test/demo deployment
2. Yes, for a multi-site cluster/single forest deployment, running multiples domain controllers
3. BIG NO, if it is an production environment running in one unique site and I will explain the reasons for that:
Root Domain Controller running on a Physical Hardware
Due the implementation of clustered Hyper-V, it is not recommended to virtualise all domain controllers. In case of connection lost to the Failover Cluster, it will fail to start as it cannot locate AD account for Cluster Hyper V Host. Microsoft Failover Cluster relies on Active Directory for authentication/authorization and it is a pre-requisite to setup failover cluster. That’s a serious matter and Microsoft released a very long articles about that.
References:
– “Always have at least one DC that is on physical hardware so that failover clusters and other infrastructure can start.” http://support.microsoft.com/kb/888794
(Article ID: 888794 – Last Review: December 29, 2011 – Revision: 13.0)
– Avoid creating single points of failure: Maintain physical domain controllers in each of your domains. This mitigates the risk of a virtualization platform malfunction that affects all host systems that use that platform.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/virtual_active_directory_domain_controller_virtualization_hyperv(WS.10).aspx
(Updated: April 11, 2011)
Note : Although it is possible to minimize the risk by having the DC running as a standalone VM, on any Cluster Hyper V, Microsoft does not recommend to run standalone VM on a cluster Hyper V
How about you. What is your thoughts on this?
Recommended articles: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/virtual_pc_guy/archive/2008/11/24/the-domain-controller-dilemma.aspx
http://www.ms4u.info/2011/05/why-you-should-not-running-domain.html
http://msincic.wordpress.com/2011/06/09/virtualize-domain-controllers-should-i-or-not/
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/888794
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd348476(v=WS.10).aspx
24 Hours in a Private Cloud
Event Description
Every organization has the power to employ cloud technologies in their own way, at their own pace and with their own terms. The use of private cloud technologies help transform how organizations manage infrastructure resources, provision applications and automate services for their business. It also helps them leverage and manage public cloud services that expand their current infrastructure and application capabilities. As an end result, organizations increase IT operational agility, improved business focus and achieve value-add economics that evolves their IT infrastructure into a strategic asset.
Over 24 hours, you will hear from top industry and technical professionals from around the world to help you better understand the private cloud technology solutions that are available today. You will hear from industry organizations about how they view the public cloud and how the role of the IT Professional will evolve as more and more organizations begin a private cloud transformation. Listen to the number of technical professionals who will be on hand talking about the required components to simplify private cloud creation and management. Talk with them and your peers about the numerous operational efficiencies that come from deploying a private cloud with the reduction of servers and the benefits of provisioning and managing virtual applications across multiple platforms.
We hope that you will come away from this event with the knowledge and experience to help you in your private cloud infrastructure decisions and be prepared to have thought-leadership based discussions focused on building and managing your organization’s agile and efficient private cloud environment.
Keynote Speakers
· Jim Reavis, Founding Director, Cloud Security Alliance
· Kevin Smith, Marketing Director, Private Cloud, Dell
· Dejan Milojicic, TBD, IEEE
Technical Areas of Focus
· Private Cloud Infrastructure
· Infrastructure Components
· Application Management
· Service Delivery and Automation
Registration link : http://bit.ly/24hipc