Archive
Dell EqualLogic and VMM 2012 support
With the release of VMM 2012 SP1 CTP2, Microsoft added support to the SMP storage provider.
Now VMM 2012 with SP1, supports the following types of storage providers:
- SMI-S CIM–XML
- SMP
Besides the new SMP provider type, the VMM 2012 SP1 release adds the following new functionality:
- Supports auto (dynamic) iSCSI target systems, such as the Dell EqualLogic PS Series. System Center 2012 – Virtual Machine Manager supported only static iSCSI target systems.
- Supports the thin provisioning of logical units through VMM. Your storage array must support thin provisioning, and thin provisioning must be enabled for a storage pool by your storage administrator
For a detailed step by step, look at my blog post https://virtualisationandmanagement.wordpress.com/2012/06/28/vmm-2012-sp1-installing-dell-equallogic-ps-series-smp-provider-new/
Infrastructure Planning and Design Guide for VMM 2012
The new IPD Guide for System Center 2012 – Virtual Machine Manager is now available to download
Infrastructure Planning and Design streamlines the planning process by:
- Defining the technical decision flow through the planning process.
- Listing the decisions to be made and the commonly available options and considerations.
- Relating the decisions and options to the business in terms of cost, complexity, and other characteristics.
- Framing decisions in terms of additional questions to the business to ensure a comprehensive alignment with the appropriate business landscape
Download the guide now: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=245473
Hyper-V DR Solution
DR is a key component of the Business Continuity Plan.
When considering DR options, virtualization is a game changer. Virtualization makes DR affordable to companies that could not afford it before. But in order to understand how DR can be optimized in a virtualized environment, it is important to understand the technical aspects, like replication functionality.
Remember : even though high availability can be achieved with clustering, this will not safeguard your businessfrom the entire data center or hosting facility going down (in case of a fire or a flood, for example). In this case you need a DR solution geographically dispersed.
Last week I started writing about Hyper-V DR solution in Windows 2012:
Keep watching this blog for the part 2…
Also, there is a good DR solution document for Windows 2008R2 here :
and here : Hyper-V in the Real World –Multi-Site DR with the System Center Suite of Products http://www.techdays.ca/contentlibrary/video/en/2011-hyper-v-in-the-real-world-–multi-site-dr-with-the-system-center-suite-of-products.aspx
Windows 2012 Hyper-V Replica : Deployment Scenarios, Functionality and Step by Step by using SSL Certificate Part I
With Windows 2012 around the corner ( first week of august 2012 ), you probably started planning the deployment already.
I am starting a series of blog posting with step by steps. The first one is about Hyper-V Replica, a real nice feature.
Hyper-V Replica. what is ?
Hyper-V replica is a new feature of Windows 2012 that enables you to replicate any Virtual Machine (yes, copy the entire VM: VHD/VHDX and configuration ) from one Hyper-V Server to another, without storage or any special hardware. You only need 2 servers running Windows 2012 Hyper-V.
You can replicate the content over the LAN or WAN (without compromising the link) by using HTTP or HTTPS protocols using SSL certificates inclusive.
Once you enable the Hyper-V Replica on the VM, the source host starts to maintain a HRL (Hyper-V Replica Log file) for the VHDs. Every 1 write by the VM = 1 write to VHD and 1 write to the HRL. Depending on bandwidth availability, the logfiles are sent to the target host every 5 minutes(setting not configurable). On the target the Hyper-V Replica mechanism run asynchronous, processing the log file in reverse order, allowing it only to store the latest writes. It replicates only the changes.
Note: After 5 minutes, if the replay hasn’t happened then you get an alert. The replica log file replication will take up to 30min to complete before going into a failed state where your intervention will be required to look at the issue and fix it.
The configurations at each site do not have to be the same with respect to server or storage hardware. Hyper-V Replica provides the option to restore virtualized workloads to a point in time depending on the Recovery History selections for the virtual machine.
Really easy to deploy and use.
Deployment Scenarios:
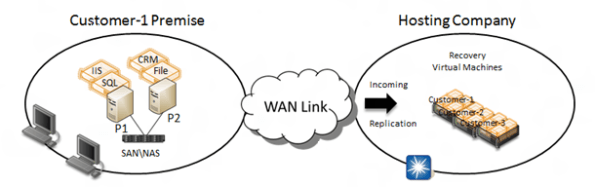
– Between 2 sites (DataCenter replication to small offices)
– Cross premises DR solution
Cluster
Hyper-V Replica works with clusters. In fact you can do the following replications:
- Standalone host to cluster
- Cluster to cluster
- Cluster to standalone host
NOTE : Hyper-V Replica is NOT an alternative to clustering. It is not intended for High Availability purposes.
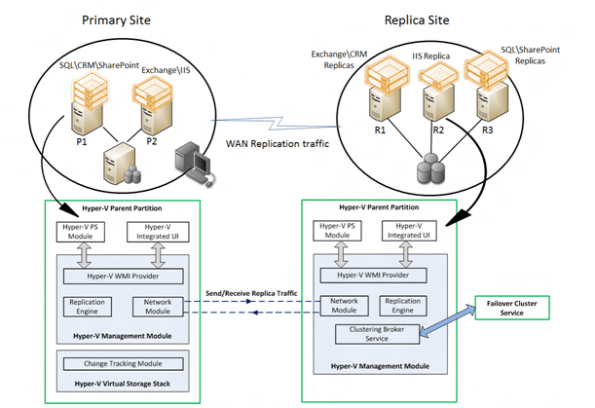
Functional description
• Replication Engine: Manages the replication configuration details and handles initial replication, delta replication, failover, and test-failover operations. It also tracks virtual machine and storage mobility events and takes appropriate actions as needed (i.e. it pauses replication events until migration events complete and then resumes where they left off).
• Change Tracking: Provides a virtual machine level change tracking mechanism on the primary server by keeping track of the write-operations, which happen in the virtual machine.
• Network Module: The Networking Module provides a secure and efficient compressed network channel to transfer virtual machine replicas between Primary and Replica site.
• Hyper-V Replica Broker role: The Hyper-V Replica Broker role is configured in a Windows Server 2012 Failover Cluster. This functionality supports seamless replication even in the event of a migration of a replica virtual machine from one cluster node to another.
• Management Experience: Hyper-V Manager UI; Failover Cluster Manager UI; PowerShell scripting; Hyper-V Replica APIs.
Step by Step – Part I
On the source Hyper-V Server
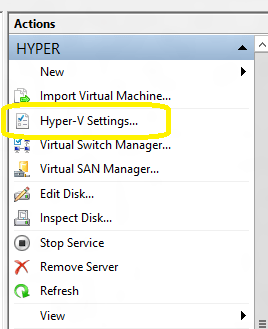
1. Open the Hyper-V Server Manager and click on the Hyper-V server. Then in the right pane, click on Hyper-V settings
2. On the Hyper-V settings page, click on Replication Configuration on the left pane
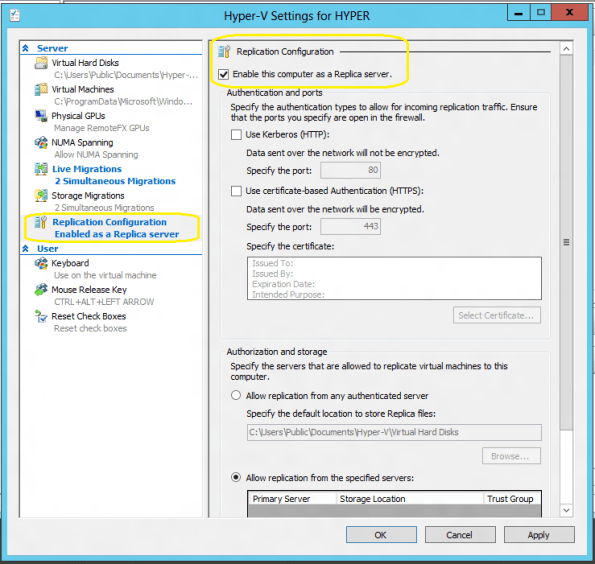
3. On the Replication Configuration, click on Enable this computer as a Replica Server
4.You have now the choose how the replication will occur : by using HTc.TP (port 80) or HTTPS (port 443, with encryption).
HTTPS: If you select HTTPS, I recommend you to buy an SSL Certificate from a trusted Certification Authority (CA), then :
a. Create an INF file for an Wildcard certificate request. Use the following example and replace the subject with the hyper-v servers domain name. Save the content in a text file as cert.inf for example.
[Version]
Signature=”$Windows NT$”
[NewRequest]
Subject = “CN=*.YOURDOMAIN.local”
Exportable = TRUE ; Private key is exportable
KeyLength = 2048 ; Common key sizes: 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384
KeySpec = 1 ; AT_KEYEXCHANGE
KeyUsage = 0xA0 ; Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
MachineKeySet = True ; The key belongs to the local computer account
ProviderName = “Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider”
ProviderType = 12
RequestType = CMC[EnhancedKeyUsageExtension]
OID=1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 ;Server Authentication
OID=1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2 ;Client Authentication
b. Create a request. Open the command prompt with Administrative rights ( run as Administrator ) and type the following:
certreq –new CERT.inf CERT.req
c. Create the CSR to submit the certificate request to an external CA
certutil -encode CERT.req CERT.csr
d.Upload the ENTIRE content of the text file CERT.csr into the external CA webpage. (could be any external trusted CA)
e.After the certificate is issued and you received the email with the certificate, open the command prompt and type the following commands to import and store the certificate on all Hyper-V servers ( source and target )
certreq -accept CERT.cer
certutil –store my
HTTP: Select : Use Kerberos HTTP
5. Configure the Authorization and storage. This includes designating a specific location to store replica virtual machine files if the default location is not to be used. Should you not desire to allow all Primary servers to be serviced, there is an option to allow only specific servers (Primary servers) to send replication requests.
If you want to allow all servers within the domain, a wildcard character can be used (e.g. *.yourdomain.local). When using a wildcard, only one storage location can be specified. If individual server entries are used, different storage locations for replica files can be configured. Complete all entries for the Primary Server, Storage Locations, and Security Tag information.
6. Click Apply or OK when finished.
Next article : configuring the target server
New Exchange 2013 to have only 2 roles : Client Access server and Mailbox Server role
Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 consists 2 server roles (reminds me of the Exchange 2000/2003 front-end/back-end split) To download the preview version : http://technet.microsoft.com/evalcenter/hh973395
Client Access server role. This role proxies connectivity for all clients, such as Microsoft Office Outlook, Outlook Web App, mobile devices, POP, and SMTP and also accepts mail from and delivers mail to other mail hosts on the Internet. Client access servers can be organized into Client Access server arrays.
It includes two different components: the Client Access service and the Front End Transport service.
The Client Access service performs the following functions:
- Provides a unified namespace, authentication, and network security.
- Handles all client requests for Exchange.
- Routes requests to the correct Mailbox server.
- Proxies or redirects client requests for legacy servers, such as Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010 Client Access.
- Enables the use of layer 4 (TCP affinity) routing.
The Front End Transport service
- This service runs on all Client Access servers and acts as a stateless proxy for all inbound and outbound external SMTP traffic for the Exchange 2013 Preview organization. The Front End Transport service doesn’t inspect message content, but it can filter messages based on connections, domains, senders, and recipients. The Front End Transport service only communicates with the Hub Transport service on a Mailbox server, and doesn’t queue any messages locally.
Mailbox server role. This role stores mailbox data, performs processing and rendering for client connections proxied by the Client Access server, and handles Unified Messaging requests. Mailbox servers can be organized into back-end clusters that use database availability groups (DAGs).
Mailbox servers house the mailbox data for the organization and perform data rendering and other operations. Mailbox servers can be grouped into back-end clusters which consist of database availability groups (DAG). Mailbox servers perform the following functions:
- Host mailbox databases.
- Provide email storage.
- Host public folder databases.
- Calculate email address policies.
- Conduct multi-mailbox searches.
- Provide high availability and site resiliency.
- Provide messaging records management and retention policies.
- Handle connectivity because clients don’t connect directly to the Mailbox servers.
- Provide all core Exchange functionality for a given mailbox where that mailbox’s database is currently activated.
- Fails over mailbox access when a database fails over.
Improved features in the Mailbox role for Exchange 2013 :
- Evolution of Exchange 2010 DAG:
- Transaction log code has been refactored for fast failover with deep checkpoint on passive database copies.
- To support enhanced site resiliency, servers can be in different locations.
- Exchange 2013 Preview now hosts some Client Access components, the Transport components, and the Unified Messaging components.
- Exchange 2013 Preview Store has been re-written in managed code to improve performance in additional IO reduction and reliability.
- Each Exchange 2013 Preview database now runs under its own process.
- Smart Search has replaced the Exchange 2010 multi-mailbox search infrastructure.
Mail Flow
The transport pipeline consists of the following services:
- Front End Transport service This service runs on all Client Access servers and acts as a stateless proxy for all inbound and outbound external SMTP traffic for the Exchange 2013 Preview organization. The Front End Transport service doesn’t inspect message content, but it can filter messages based on connections, domains, senders, and recipients. The Front End Transport service only communicates with the Hub Transport service on a Mailbox server, and doesn’t queue any messages locally.
- Hub Transport service This service runs on all Mailbox servers and is virtually identical to the Hub Transport server role in previous versions of Exchange. The Hub Transport service handles all SMTP mail flow for the organization, performs message categorization, and performs message content inspection. Unlike previous versions of Exchange, the Hub Transport service never communicates directly with mailbox databases. That task is now handled by the Mailbox Transport service. The Hub Transport service routes messages between the Mailbox Transport service, the Hub Transport service, and the Front End Transport service.
- Mailbox Transport service This service runs on all Mailbox servers and consists of two separate services: the Mailbox Transport Submission service and Mailbox Transport Delivery service. The Mailbox Transport Delivery service receives SMTP messages from the Hub Transport service, and connects to the mailbox database using an Exchange remote procedure call (RPC) to deliver the message. The Mailbox Transport Submission service connects to the mailbox database using RPC to retrieve messages, and submits the messages over SMTP to the Hub Transport service. The Mailbox Transport service doesn’t queue any messages locally.
Quick note: Although not confirmed by Microsoft, I will not be surprised with a debut in the fourth quarter of 2012.
For more info about Exchange 2013 : http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/fp179701.aspx
Convert Vmware virtual machines to Hyper-V with Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter
Convert and deploy virtual machines to Hyper-V with Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter
The Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter (MVMC) Release Candidate is now available! This release allows you to convert and deploy virtual machines from VMware hosts to Hyper-V hosts running Windows Server 2012 Release Candidate and Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 Release Candidate. The MVMC Release Candidate also adds virtual network interface cards (NICs) to the converted virtual machine on Hyper-V and configures the dynamic memory on the converted virtual machine.
MVMC supports converting virtual machines using the following guest operating systems:
- Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2
- Windows Server 2003 R2 with Service Pack 2
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows 7
The Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter converts VMware virtual machines created with:
- VMware vSphere 4.1
- VMware vSphere 5.0
To virtual machines for:
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 Hyper-V
- Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 R2 SP1
Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter key features:
- MVMC provides a quick, low-risk option for VMware customers to evaluate Hyper-V.
- MVMC converts the virtual disks and the VMware VMs configuration, such as memory, virtual processor, and other machine settings from the source.
- Use this tool to uninstall VMware tools on the source VM and install the Hyper-V Integration Services as appropriate.
- An easy-to-use wizard-driven GUI simplifying VM conversion is also included.
- MVMC supports offline conversions of VMware virtual hard disks (VMDK) to a Hyper-V based virtual hard disk file format (VHD).
- MVMC includes a scriptable Command Line Interfaces (CLI) for performing machine conversion and offline disk conversion which integrates with datacenter automation workflows, such as those authored and executed within System Center Orchestrator. The command line can also be invoked through PowerShell.
Download the Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter Release Candidate.
Get ready for Windows Server 2012 with new Solution Accelerators : MAP Toolkit
Accelerate Windows Server 2012 readiness with MAP 7.0!
Get ready for Windows Server 2012 with the Microsoft Assessment and Planning (MAP) Toolkit 7.0. The latest version of the MAP Toolkit adds several new planning scenarios that help you build for the future with agility and focus while lowering the cost of delivering IT. New capabilities allow you to understand your readiness to deploy Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 in your environment.
Windows 2012 Hyper-V RTM to be released first week of August 2012
Microsoft announced at WPC in Toronto, both server and client announced RTM (first week of August) and GA(Sept for Server, Oct for client) timing publicly:
“Windows 8/Windows 2012 is on track to Release to Manufacturing (RTM) the first week of August. For enterprise customers with Software Assurance benefits, they will have full access to Windows 8 bits as early as August. Additionally, she noted that RTM is when we’ll be turning on the commerce platform so that developers can start earning money for their apps ”
VMM 2012 SP1: Installing and Configuring Dell EqualLogic PS Series SMP provider : NEW
VMM 2012 SP1 supports the same storage arrays that were supported in VMM 2012, plus the SMP provider. For more info : (http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/4583.scvmm-2012-storage-and-load-balancer-provider-downloads-en-us.aspx)
Below are the steps to install and connect your Dell EqualLogic PS Storage to VMM 2012 SP1 using the new SMP Provider
1. Install the Dell EqualLogic Host Integration Tools 4.5 on the VMM management server, and then restart the server.
Note: Dell EqualLogic Host Integration Tools compatible with SCVMM 2012 SP1 is planned for availability late this year. The new release is the next step in integrating Microsoft applications with EqualLogic storage arrays.
Contact Dell to obtain the Dell EqualLogic Host Integration Tools.
2. Start the VMM command shell as an administrator. Import the EqualLogic PowerShell Tools module and then add the storage provider by using the New-EqlGroupAccess cmdlet. Then, import the storage provider into VMM by using the Import-SCStorageProvider cmdlet. For example:
PS C:\> Import-Module -Name “C:\Program Files\EqualLogic\bin\EQLPSTools.dll”
PS C:\> New-EqlGroupAccess -GroupName “EqlGroup” -GroupWKAddress 10.0.0.0 -GroupMKAddress 10.0.0.1 -UserName Administrator -Password “AcctPassword”
PS C:\> Import-SCStorageProvider
It may take a while depending on the number of storage pools and logical units that already exist on the array.
To verify whether the provider was imported, in the Fabric workspace of the VMM console, in the Fabric pane, expand Storage, and then click Providers.
In the Providers pane, verify that the provider appears, with a status of Responding.
4. To bring the storage pools under management and to assign classifications, follow these steps:
a. In the Arrays pane, right-click the array, and then click Properties.
b. In the Array Name Properties dialog box, click the Storage Pools tab.
c. Under Storage Pools, select the check box next to each storage pool that you want VMM to manage.
d. Under Classification, select an existing classification or create a new one. To create a new one, click Create classification, enter a classification, click Add, and then in the Classification list, select the new classification.
e. When you are finished, click OK.
f. Open the Jobs workspace, and verify that the Sets Storage Array job completes.
5. Verify that you can create and delete logical units. To do this, follow these steps:
a. In the Fabric pane, under Storage, click Classifications and Pools.
b. In the Classifications, StoragePools, and Logical Units pane, click the desired storage pool.
c. On the Home tab, click Create Logical Unit.
d. In the Create Logical Unit dialog box, enter a name, optional description, and size.
e. If the storage pool is configured to support thin provisioning, optionally click Create thin storage logical unit with capacity committed on demand, and then click OK.
When the job completes, in the Classifications, StoragePools, and Logical Units pane, verify that the new logical unit is listed under the pool.
f. To remove the logical unit, click the logical unit. Then, on the Home tab, in the Remove group, click Remove. Review the warning message, and then click OK to continue. Verify that the logical unit is removed from the list.
To configure storage on a Hyper-V host, follow the procedures in in the System Center 2012 – Virtual Machine Manager topic How to Configure Storage on a Hyper-V Host. Try assigning a logical unit to a host, with an assigned drive letter.
Hyper-V Windows 2012 : High Availability and Resiliency : new enhancements
There are a number of new enhancements that ensure key workloads are resilient, and protected.
• Hyper-V Replica – Asynchronous, application-consistent virtual machine replication and it does not depend on any hardware vendor. You can establish an Hyper-V Replica between 2 separated physical locations without a storage. It permits asynchronous replication of Hyper-V virtual machines between two locations for business continuity and failure recovery.
• Incremental Backups – True differential disk backups of virtual hard disks to help ensure that the data is backed up and restored when necessary. It also reduces storage costs because it backs up only what has changed, not the entire disk.
• NIC Teaming – Provides increased reliability and performance for virtual machines and now does not depends on manufacturer drivers.
• Hyper-V Clustering Enhancements – Unmatched scale and flexibility for virtualized infrastructures:
• Unmatched Scale – Windows Server 2012 support up to 64 physical nodes and up to 4,000 virtual machines in a single cluster providing scalability and flexibility for key virtualized workloads.
• Flexible Virtual Machine Guest Clustering – Provides not only iSCSI guest clustering support, including MPIO, but also enables the use of Virtual Fibre Channel adapters within the virtual machine allowing workloads access to storage area networks using fiber channel fabric. In addition, a virtual fibre channel enables IT to cluster guest operating systems over Fibre Channel providing HA for workloads within VMs and utilize the built-in Windows multi-path I/O (MPIO) for high-availability and load balancing on the storage path. By employing MPIO and Failover Clustering together as complimentary technologies, users are able to mitigate the risk of a system outage at both the hardware and application levels.
• Highly Secure Clustered Storage – Hyper-V, Failover Clustering and BitLocker now work in concert to create the ideal and secure platform for private cloud infrastructure. Windows Server 2012 Cluster disks that are encrypted using BitLocker Drive Encryption enable better physical security for deployments outside secure data centers, providing a critical safeguard for the cloud and helping protect against inadvertent data leaks
• Enhanced Cluster Shared Volumes – Cluster Shared Volume 2.0 (CSV). CSV has been greatly enhanced in a number of ways. From a usability standpoint, CSV is now a core Failover Clustering feature, with simplified administration and management. To support up to 64 nodes in a cluster, CSV has been improved in aspects of both performance and scalability. In terms of integrating with our partners, CSV has specifically been enhanced to work out of the box with storage filter drivers such as those used by: anti-virus, data protection, backup and storage replication ensuring a more seamless integration with existing investments.
• 3 Levels of Availability – Bringing higher availability to workloads that do not support clustering. It does this by providing a light-weight, simple solution to monitor applications running in the VMs and integrating with the host. By monitoring services and event logs inside the virtual machine, Hyper-V and Failover Clustering can detect whether the key services that a virtual machine provides are healthy and provide automatic corrective action such as restarting the virtual machine or restarting a service within the VM. This is in addition to the already existing virtual machine failover capabilities should a host fail, or the virtual machine itself become unresponsive.
• Cluster-Aware Updating – An in-box end-to-end solution for updating Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V Failover Clusters, helping customers to preview, apply, and report on updates, all with zero downtime to the virtual machines.
• Virtual Machine Failover Prioritization – Virtual machine priorities can now be configured to control the order in which specific virtual machines failover or start. This ensures higher priority virtual machines are given the resources they need and lower priority virtual machines are given resources as they are available.
• Affinity (and Anti-Affinity) Virtual Machine Rules – Administrators can now configure partnered virtual machines so that at failover, the partnered machines are migrated simultaneously. For example, administrators can configure their SharePoint virtual machine and the partnered SQL Server virtual machine to always failover together to the same node. Administrators can also specify that two specific virtual machines cannot coexist on the same node in a failover scenario.
How Does VmWare compare?
| Capability | Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V |
VMware ESXi 5.0 |
VMware vSphere 5.0 Enterprise Plus |
| Incremental Backups |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
| VM Replication |
Yes |
No |
vCenter SRM |
| NIC Teaming |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Integrated High Availability |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
| Guest OS Application Monitoring |
Yes |
N/A |
No |
| Cluster-Aware Updating |
Yes |
N/A |
Yes |
| Failover Prioritization |
Yes |
N/A |
Yes |
| Affinity & Anti-Affinity Rules |
Yes |
N/A |
Yes |
What are you waiting for? start today your own POC of Windows 2012 !