Archive
Client Hyper-V in Windows 8
Windows PowerShell scripts for managing virtual machines that you create using Client Hyper-V are fully compatible in with Windows Server 8 Hyper-V.
There a few features included in Windows Server 8 Hyper-V that are not included in Client Hyper-V. These include: the remote FX capability to virtualize GPUs (software GPU in RDP 8), Live VM migration, Hyper-V Replica, SR-IOV networking, and synthetic fiber channel.
HARDWARE : Hyper-V requires a 64-bit system that has Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). GB RAM is required. The RAM on your Client Hyper-V machine is allocated and de-allocated dynamically as required by the VMs. You can run several VMs on a Client Hyper-V machine (also called a “host”) that has the minimum 4GB of RAM, but you will need additional RAM for 5 or more VMs, depending on the RAM requirements for each VM.
Client Hyper-V supports server Hyper-V’s “Live Storage Move” capability. This means you can use your VMs fairly independent of the underlying storage. You can move VMs to and from one local drive to another, to a USB stick, or to a remote file share without needing to stop the VM.
To Enable using GUI:
-
On the Control Panel click “Programs”, and then click “Programs and Features”
-
Click “Turn Windows features on or off”
-
Click “Hyper-V”, and then click “OK”, and then click “Close”
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature –FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -Restart
Important :
You must restart your machine, not just reboot, to complete installation
For more info: Windows 8 Client Hyper-V wiki page (FWLINK) (http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/7704.client-hyper-v-survival-guide.aspx)
Windows 8 Consumer Preview are now live
The Windows 8 Consumer Preview bits are now live. Everything you need to know, including links and information about the download is on the Springboard Series for Windows 8 on TechNet. Also, the Windows 8 TechNet forums are now live.
http://technet.microsoft.com/windows/windows-8
- Windows 8 Consumer Preview Product Guide
Download a detailed guide to the new and improved features in Windows 8 including AppLocker, BitLocker, Windows To Go, measured boot, and Client Hyper-V. - Windows To Go Technical Overview
Learn how Windows To Go can help you provide users with bootable USB storage devices containing a copy of Windows 8, along with their business apps, data, and settings. - Frequently Asked Questions: Managing the Windows Store
Get answers to frequently asked questions about managing end user access to, and usage of, the Windows Store within your organization. - The Windows 8 User Experience
Learn more about application, Web, and cloud features for end users. - Windows 8 Consumer Preview Technical Forums
Get help with questions on installation and setup, networking, compatibility, security, performance, and more
Hyper-V. New Linux Integration Services 3.2
This release includes the following features:
-
Synthetic Mouse Support: Finnaly ! The virtualized mouse device is no longer bound to the VMConnect window, and can now be used with a RDP session, which means that you no longer need to install a separate package to get integrated mouse support, and will not have to worry about the mouse being captured by the virtual machine.
-
Merged Device Drivers: We now present a single device driver for both IDE and SCSI devices (hv_storvsc).
-
Windows 8 Fix: The synthetic network device (hv_netvsc) can now be used with a Windows 8 host, eliminating the hang on boot that was previously seen.
-
SCVMM Fix: This release fixes the issue as described inKB2586286.
-
Improved Setup Experience: Users now only need to run install.sh (as root) to automatically detect the correct architecture and install the appropriate drivers
In addition, :
- The driver applied to guest virtual machines running Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 6.1 (architecture x 86 and x 64) and CentOS 6.0 (architecture x 86 and x 64). For earlier version should be used components integration version 2.1
- In fact, it’s modified drivers in the Linux kernel 3.2, but can work with the Linux kernel 2.6.32, shipped with Red Hat and CentOS
BIG NOTE: Microsoft is working with the sponsors of the Linux distros and in the future a list of officially supported distributions will be expanded.
You can download them directly from here: http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=28188
Running Windows 8 Preview as Hyper-V Windows 2008R2 Virtual Machine
If you are planning to run Windows 8 as a Virtual Machine under your current Hyper-V Windows 2008R2 server, here is an update that enables the Windows Developer Preview or Windows Server Developer Preview to be hosted in a Hyper-V virtual machine on Windows Server 2008 R2:
Hotfix: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;2526776
Without this hotfix you may experience one or more of the following issues:
- The Windows Developer Preview or Windows Server Developer Preview virtual machine stops responding.
- The Windows Server 2008 R2 host computer displays a stop error message and restarts automatically. This behavior brings down all other running virtual machines together with the host computer
Hyper-V Replica Setup (Step by Step)
Let’s start by configuring the Hyper-V Replica on the Recovery Server
( Quick note: Hyper-V Replica it is only possible on Windows 8 Server version. It does not exist on Desktop Version )
1. Open the Hyper-V Manager, under Replication Configuration, Select Enable this computer as replica server2. Specify Authentication mode :Integrated Windows(Kerberos) or Certificate
3. Configure Authorization list :
– Type the name of the primary server
– Specify the location to be used as primary VM Configuration (can be local or an smb share)
4. Configure the Firewall by adding the inbound rule for the used ports
5. Enable Remote WMI
Now let’s configure the Primary Server
1. Open the Hyper-V Manager and Select the VM to replicate and click on Settings. Under Management, Replication
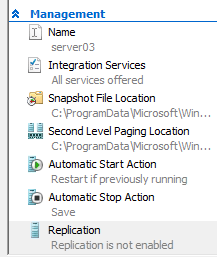

2. Specify the Recovery Server Name to replicate to ( e.g. hypervreplica.mylab.local)
3. Specify the Autentication mode ( selected when you configured the Recover Server )
4. Specify if Compression will be enabled or disabled
5. Select the VHD’s that will be excluded of the process
6. Select the Replication Parameters:
– Recovery ( in hours )
– Application Consistent frequency

7. Select the Initial Replication Mode:
– Over Network : once sucessfully connection established, the primary server will sends the VHD files to the Recovery Server. ( can be scheduled )
– Off the Network : ( my recomendation ) The Hyper-V Replica will copy the VHD’s to a specified location which can be an external Hard Disk. You can after that copy the files back to the storage location specified during the Recovery Server Setup
– Using Backup
That’s it. The VM will then be created (powered off) on the recovery server once finished and after that the Primary Server, based on replication frequency will send the changes to the Recovery Server
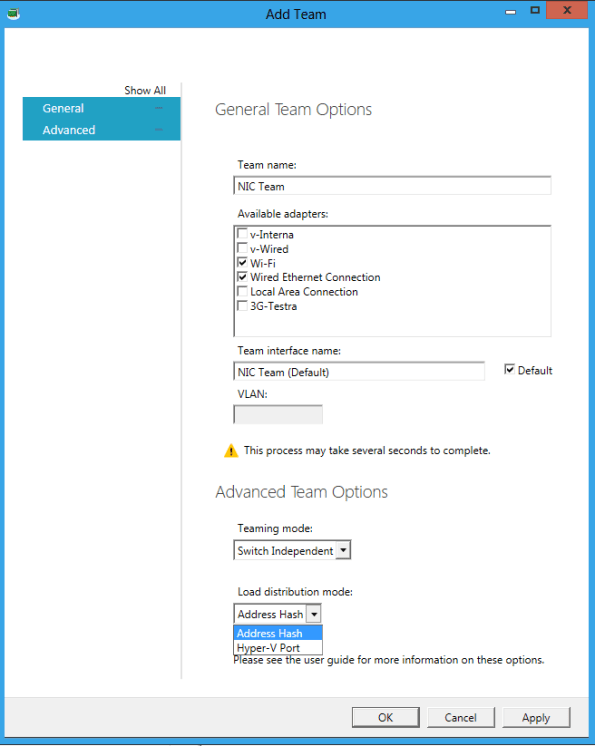
Windows 8 Server : native support for NIC Teaming
Windows 8 will come with native NIC Teaming, which means that we don’t need to pre-install or configure any software provided by the NIC vendor for the NIC TEAMING work.
Now you can team 2 or more NIC’s even if they are from different vendors configured as NIC Teaming and better, you can expose that NIC to Hyper-V Virtual Machines. This is really cool and one of the most wanted features.
The scenarios for application of the feature in production are infinite now, especially In High Availability environments. But please be aware that is the preview version! Much more still to come!
As an example, I installed Windows 8 with the NIC teaming configured using the Wireless NIC and the Wired NIC, then I went to the Hyper-V Manager and I created an Virtual Switch pointing to the NIC Team. How cool is that?
Windows 8 : Hyper-V’s “Live Storage Move”
Hyper-V’s “Live Storage Move” capability helps your VMs to be fairly independent of the underlying storage. With this, you could move the VM’s storage from one local drive to another, to a USB stick, or to a remote file share without needing to stop your VM.
This feature is helpfull for fast deployments, when for you need example a VM quickly, you can then start one from a VM library maintained on a file share and then move the VM’s storage to another local drive.
Other good example will be when the physical disk is full. You will then quickly be able to move the VM’s storage to other drive.
For storage, you can add multiple hard disks to the IDE or SCSI controllers available in the VM. You can use Virtual Hard Disks (.VHD or .VHDX files) or actual disks that you pass directly through to the virtual machine. VHDs can also reside on a remote file server, making it easy to maintain and share a common set of predefined VHDs across a team.
More info: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2011/09/07/bringing-hyper-v-to-windows-8.aspx
Windows 8 Desktop Client version will have Hyper-v x64-bit VM’s
Microsoft announced that the upcoming Windows 8 desktop version will have Hyper-v which will support x64-bit VM’s
Hyper-V requires a 64-bit system that has Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). SLAT is a feature present in the current generation of 64-bit processors by Intel & AMD.
You’ll also need a 64-bit version of Windows 8, and at least 4GB of RAM. Hyper-V does support creation of both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems in the VMs.
Plus, Hyper-V’s dynamic memory allows memory needed by the VM to be allocated and de-allocated dynamically (you specify a minimum and maximum) and share unused memory between VMs.
As for user experience with VMs, Windows provides two mechanisms to peek into the Virtual Machine: the VM Console and the Remote Desktop Connection.
The VM Console (also known as VMConnect) is a console view of the VM. It provides a single monitor view of the VM with resolution up to 1600×1200 in 32-bit color. This console provides you with the ability to view the VM’s booting process.
Features or applications that depend on specific hardware will not work well in a VM. For example, Windows BitLocker, Measured Boot, games or applications that require processing with GPUs, also, applications relying on sub 10ms timers, i.e. latency-sensitive high-precision apps such as live music mixing apps, etc. could have issues running in a VM.
The root OS is also running on top of the Hyper-V virtualization layer, but it is special in that it has direct access to all the hardware. This is why applications with special hardware requirements continue to work unhindered in the root OS but latency-sensitive, high-precision apps could still have issues running in the root OS.
Windows 8 : Windows Explorer gets new interface : now with ribbon ( office 2010 like )
Windows 8 is comming with lot of good surpises. I just heard about the new ribbon:
The new ribbon
The Home tab is focused on the core file management tasks, and we’ve put all the major file management commands there in prominent locations: Copy, Paste, Delete, Rename, Cut, and Properties. We’ve also given new prominence to two popular heritage features, Move to and Copy to, along with exposing a hidden gem, Copy path, which is really useful when you need to paste a file path into a file dialog, or when you want to email someone a link to a file on a server.
The Home tab is the heart of our new, much more streamlined Explorer experience. The commands that make up 84% of what customers do in Explorer are now all available on this one tab:

Overlay showing Command usage % by button on the new Home tab
The Share tab is for sharing files by typical methods like zipping them up and emailing them to a friend, or burning them to optical media. Or you can quickly share files with other people in your home group or your network domain. It also provides one-click access to the ACLs for the currently highlighted file.
Source : http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2011/08/29/improvements-in-windows-explorer.aspx
Windows Server 8 Hyper-V: first public glimpse
What is comming in the new version?
16+virtual processors within a Hyper-V VM, to support large scale up workloads.
Hyper-V Replica. Today, replication is complex to configure and often requires expensive proprietary hardware. Hyper-V Replica is asynchronous, application consistent, virtual machine replication built-in to Windows Server 8. With Hyper-V Replica, you can replicate a virtual machine from one location to another with Hyper-V and a network connection. Hyper-V Replica works with any server vendor, any network vendor and any storage vendor. In addition, we will provide unlimited replication in the box.
Microsoft also is going to allow Windows Server 8 users to replicate unlimitedly without charging additional fees per virtual machine. On the other hand, VMware with their upcoming version of Site Recovery Manager (SRM) is going to charge customers a per VM replication to replicate. This is going to be interesting….
Several others new features coming in the next version of Windows Server. Stay Tuned…