Archive
The network connection of a running Hyper-V virtual machine is lost under heavy outgoing network traffic on a Windows Server 2008 R2-based computer
If you’ve deployed your Virtual Machine on Hyper-V R2 and noticed that a connection between the guest and the virtual switch starts "acting odd", perfoms poorly or becomes disconnected entirely, you may want to apply this update:
Prerequisites
To apply this hotfix, your computer must be running Windows Server 2008 R2.
Additionally, you must have Hyper-V role installed on your computer.
Restart requirement
You have to restart the computer after you apply this hotfix
Steps to get you ready for virtualization
Scenarios driving virtualization:
- Server consolidation – lower data center costs
- Application migration
- Increased IT agility – reduced deployment and provisioning time
- Software development and training
Steps to get you ready for virtualization:
Step 1. Determine Whether Virtualization Is Appropriate:
Compatibility : Determine whether the workload can run in a virtualized environment.
Supportability : Determine whether the workload is supported in a virtualized environment. It might be necessary to verify third-party vendors’ policies for deployment of the workload on all the virtualization technologies that will be used.
Licensing : Determine whether the workload can be licensed for use in a virtualized environment.
Business benefits : Determine the business reasons for virtualizing the workload and the related benefits. Potential benefits include cost savings, reduced deployment time, and reduced administration costs.
Step 2. Categorize the Workload
Workloads designed for server operating systems typically have different resource requirements and different levels of interactivity than those designed for client workloads.
Step 3. Select Server Hardware or Server Software Virtualization
Microsoft offers two server virtualization products:
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V, which provides server hardware virtualization.
Virtual Server 2005 R2 SP1, which provides server software virtualization.
Step 4. Determine Client Connectivity
Option 1: Connected Client
Client computers that will always be connected to the network when running a particular workload can rely upon the network in order to access their applications and data. Typical scenarios include corporate desktop computers and kiosks as well as some computers used in remote offices and home offices. This option should be selected when client computers will have reliable network connections and do not need to run applications when not connected to the network. If the client will always be connected, proceed to Step 5: “Determine Workload Location.”Option 2: Disconnected Client
Client computers that must have the ability to run virtualized applications while disconnected from the network will require versions of the applications that are resident on the disconnected computer. These options are most useful for situations in which users need only occasional access to applications while traveling or when network connections are unreliable. If the client may run disconnected, proceed to Step 7: “Choose Application Virtualization or Virtualization on the Desktop.”
Step 5. Determine Workload Location
Option 1: Centralized Workload
If the workload can be centrally managed and efficiently run from a server, consider a centralized approach to application virtualization. This is beneficial when the workload configuration needs to be tightly controlled or when resources must be centrally managed. It allows for easier deployment and management of workloads.
Proceed to Step 6: “Select Desktop or Session Virtualization.”Option 2: Decentralized Workload
Some workloads cannot be run from a central server or they require individualized configuration or access to local system resources to run efficiently. These workloads should be deployed using a virtualization method that can be distributed to desktop systems.
Proceed to Step 7: “Choose Application Virtualization or Virtualization on the Desktop.”
Step 6. Select Desktop or Session Virtualization
Option 1: Desktop Virtualization
VDI provides virtualized desktops that can run a wide variety of client or server operating systems since they are hosted in VMs on the Windows Server 2008 operating system. Since there will normally be only one user on the client’s operating system, he or she may be granted administrative rights.Option 2: Session Virtualization
The client’s applications are run directly on the Windows Server 2008 operating system. There will normally be many connected clients that share the operating system and the applications, so clients cannot be granted administrative rights.
All applications that are installed on the server must be able to run on the same Windows Server 2008 operating system. Any incompatibilities should be managed by using another application virtualization technology, such as Microsoft Application Virtualization.
Step 7. Choose Application Virtualization or Virtualization on the Desktop
Option 1: Application Virtualization
Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V) provides a method for installing applications into a virtualized environment via MSI or streaming them on-demand. Application processing will occur on client computers. App-V requires that client computers have a complete client operating system that supports the virtualized applications, as well as meeting the hardware requirements for applications that will be deployed and executed on that computer. Sufficient network bandwidth for deploying applications must also be available.
See the Infrastructure Planning and Design Guide for Microsoft Application Virtualization at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=160978.Option 2: Virtualization on the Desktop
Virtual PC allows users to run entire client operating systems on their local computers. In order to support this configuration, the client computer must have sufficient CPU, memory, disk, and network resources to support the base Windows operating system, as well as resources for each of the VMs that will be supported.
Virtual PC provides support for running legacy applications and operating systems. Windows XP Mode provides a tailored Windows XP VM that runs on Virtual PC in Windows 7.
Users can create a wide variety of different VMs and can start and stop them as needed. This solution is particularly helpful for software developers and testers who often require access to multiple different platforms.
Additional Considerations
After selecting the most appropriate virtualization technology for each requirement, decide how the virtualized environment will be managed, and determine whether virtualization technologies should be used separately or together in combination.
Managing the Virtualization Environment
To help you with the challenges of managing a virtualized environment you will need the System Center Virtual Machine Manager and MED-V. Some of the key benefits of them, include:
- Optimal consolidation of under-utilized physical servers.
- Rapid provisioning of new VMs.
- Maximization of data center resources.
- Integration with System Center Operations Manager 2007.
More info : Microsoft Infrastructure Planning and Design (IPD) Guide for Selecting the Right Virtualization Technology
Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 Released
In the following sections I will list some of the new functionality that we have added into TMG and will cover some of our infrastructure investments.
Secure Web Gateway
Forefront TMG is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG) that improves security enforcement by integrating multiple detection technologies such as URL filtering, Anti Malware, and intrusion prevention into a single, easy-to-manage solution. We have seen a lot of interest in the features that comprise this solution, so here is some information on what they do and how:
URL Filtering: URL Filtering allows controlling end-user access to Web sites, protecting the organization by denying access to known malicious sites and to sites displaying inappropriate or nonproductive materials, based on URL categories. TMG features over 80 URL categories including security-oriented categories, productivity-oriented and liability-oriented categories. Forefront TMG uses Microsoft Reputation Services (MRS), a cloud-based categorization system hosted in Microsoft data center. To ensure the best bandwidth utilization and low latency, Forefront TMG has implemented a local URL cache.
Anti Malware: Stopping malware on the edge significantly decreases the possibility that a virus will hit a computer with anti-virus signatures that are not up-to-date or a test computer without an anti-virus to protect it. TMG has integrated the Microsoft Anti Malware engine to provide world class scanning and blocking capability on the edge.
Network Inspection System (NIS): NIS is a generic application protocol decode-based traffic inspection system that uses signatures of known vulnerabilities, to detect and potentially block attacks on network resources. NIS provides comprehensive protection for Microsoft network vulnerabilities, researched and developed by the Microsoft Malware Protection Center – NIS Response Team, as well as an operational signature distribution channel which enables dynamic signature snapshot distribution. NIS closes the vulnerability window between vulnerability disclosures and patch deployment from weeks to few hours.
In addition, we have introduced HTTPS scanning to enable inspection of encrypted sessions, eased the deployment and management with a set of easy to use wizards and significantly improved logging and reporting to provide full visibility into how your organization is accessing the web and whether it’s compliant with your organization’s policy.
VPN, Firewall, Email Protection and Infrastructure.
We have also made significant investments to ensure that we keep delivering top notch VPN and Firewall functionality. We made quality improvements in Web Caching and made sure it works well with the new Windows 7 BranchCache feature. We have added several new features, among them: Email Protection, ISP redundancy, NAP integration with VPN role, SSTP, VoIP traversal (SIP support), Enhanced NAT, SQL logging and Updated TMG Client (previously known as the Firewall Client). In addition TMG was built as a native 64bit product that supports Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server 2008 SP2, allowing better scalability and increased reliability.
These improvements are in direct response to your requests and protection needs. We firmly believe that listening to your voice makes our product better! We are looking forward to hearing what you think about TMG 2010 as you test and deploy in your own environment.
So go ahead and download it today to try it out!
How to determine the right Server Virtualization scenarios for your IT needs
MAP is a powerful inventory, assessment, and reporting tool that can securely run in small or large IT environments without requiring the installation of agent software on any computers or devices.
The server virtualization scenarios help you identify underutilized resources and the hardware specifications needed to successfully consolidate your servers using Microsoft Hyper-V technology.
Additionally, the toolkit can help you identify unmanaged assets, Microsoft SQL Server® components and virtual machines in your environment
Download here : Download the Microsoft Assessment and Planning Toolkit
New features in the Remote Desktop Client RDC 7.0
The RDC 7.0 client can be used to connect to legacy terminal servers or to remote desktops as before. However, the new features that are mentioned in this article are available only when the client connects to a remote computer that is running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2
Web Single Sign-On (SSO) and Web forms-based authentication
For security, Web SSO requires remote applications to be signed using a certificate from a trusted issuer.
Access to personal virtual desktops by using RD Connection Broker
Access to virtual desktop pools by using RD Connection Broker
Status & disconnect system tray icon
RD Gateway-based device redirection enforcement
RD Gateway system and logon messages
RD Gateway background authorization & authentication
RD Gateway idle & session time-outs
NAP remediation with RD Gateway
Windows Media Player redirection
Bidirectional audio
Multiple monitor support
Note For connections with multiple monitor support enabled, AeroGlass support is currently not supported and will be turned off.
Enhanced video playback
Functionality available only when connecting from Windows 7 to Windows 2008 R2
Language Bar docking
RemoteApp allows users to use their docked Language Bar with their RemoteApp applications just as they do with the local applications.
This productive functionality was previously unavailable. Instead, users had to use the floating Language bar.
Remote application task scheduler
Remote application task scheduler functionality automatically starts remote applications on the Remote Desktop client required by the user. The client computer must have Windows 7 installed to use this feature.
Aero Glass support
Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 did not support Aero Glass remoting for sessions. This is now supported in Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services, but is incompatible with multi-monitor support.
Start applications and desktops from ‘RemoteApp and Desktop Connections
Users can subscribe to all of their RemoteApp programs and desktops which are then listed in their local Start menu. The list is automatically updated as items are added or deleted
Update for Windows Vista, x86-based versions

Download the Update for Windows Vista for x86-based systems package now. (http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyId=ac7e58f3-2fd4-4fec-abfd-8002d34476f4)
Update for Windows Vista, x64-based versions

Download the Update for Windows Vista for x64-based systems package now. (http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyId=11e7a081-22a8-4da7-a6c5-cdc1ac51a1a4)
Update for Windows XP, x86-based versions

Download the Update for Windows XP for x86-based systems package now. (http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyId=72158b4e-b527-45e4-af24-d02938a95683)
SCVMM : Windows 7 Template Creation Error : –2147024864
Here are the Release Notes from the RC that discusses this issue. It’s about half way down under the System Preparation Tool section
http://download.microsoft.com/download/F/D/B/FDBFC5A5-51CD-4C8D-9F18-7BCC3810498E/Windows%207%20RC%20Release%20Notes.htm
SCVMM takes care of applying sysprep.
sysprep 1.1 is here:
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=0C4BFB06-2824-4D2B-ABC1-0E2223133AFB&displaylang=en
and Server 2003 is here:
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=93F20BB1-97AA-4356-8B43-9584B7E72556&displaylang=en
and XP is here:
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=673A1019-8E3E-4BE0-AC31-70DD21B5AFA7&displaylang=en
But you most likely want the "Deployment Toolkit"
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=3bd8561f-77ac-4400-a0c1-fe871c461a89&displaylang=en&Hash=HD%2f3UQpbIQnCaKf%2fth6Sfnc8bHXTDgeIgX6nNzQZVmYzRXFYx9%2bZHVDniseSpp6wwteVT%2bTXF6qj3bTF39cAsw%3d%3d
Moving R2 differencing disk to Windows Server 2008 : Need Hotfix
Hotfix needed to move R2 differencing disk to Windows Server 2008
In Windows Server 2008 R2 there was a minor change to the format of differencing virtual hard disks. As a result you will need to apply an update to Windows Server 2008 if you want to move differencing disks from Windows Server 2008 R2 to Windows Server 2008.
You can download this update from here:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/971677
Note that this applies to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 SP2 (not to Windows Server 2008 R2). If you do not have this update installed and you try to use a differencing disk created with Windows Server 2008 R2 you will receive an error message that states that the virtual hard disk is corrupted or unreadable.
Posted by Ben ( Virtual PC Guy )
http://blogs.msdn.com/virtual_pc_guy/archive/2009/10/16/hotfix-needed-to-move-r2-differencing-disk-to-windows-server-2008.aspx
Remote Desktop Load Simulation Tools : VDI Deployment sizing tool
In a server-based computing environment, all application execution and data processing occur on the server.
Storage. New version of StarWind allow Cluster Failover Active-Active
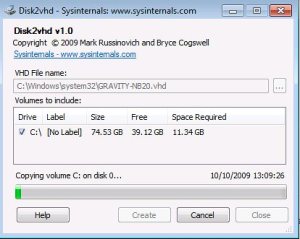
Migrating Physical Machine into Virtual Machines by using command line
- Virtual PC supports a maximum virtual disk size of 127GB. If you create a VHD from a larger disk it will not be accessible from a Virtual PC VM.
- Do not attach to VHDs on the same system on which you created them if you plan on booting from them. If you do so, Windows will assign the VHD a new disk signature to avoid a collision with the signature of the VHD’s source disk. Windows references disks in the boot configuration database (BCD) by disk signature, so when that happens Windows booted in a VM will fail to locate the boot disk.