Archive
SCDPM 2010: Backup Machines in a Workgroup/DMZ. How to protect your Hyper-V Servers that are not domain joined
One of the greatest features of SCDPM 2010 is the ability to backup machines that are in a workgroup/DMZ/untrusted domain. This is good for example because some of my Hyper-V serveres are in the workgroup mode.
1. Install the DPM agent on the server you want to protect. Copy the agent folder to that server and double click the EXE and wait for the message to tell you that the agent was installed successfully. You then might need to reboot.
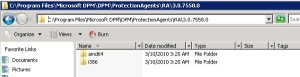
- x86 : <installation drive>Program FilesMicrosoft DPMDPMProtectionAgentsRA3.0.7558.0i386DPMAgentInstaller_x86.exe
- x64 : <installation drive>Program FilesMicrosoft DPMDPMProtectionAgentsRA3.0.7558.0amd64DPMAgentInstaller_x64.exe
Also, copy the SetDPMServer.exe from <installation drive>Program FilesMicrosoft Data Protection ManagerDPMbin
Once the agent is installed it needs to be configured. This is done using SetDPMServer.exe
2. Run SetDPMServer.exe with following arguments, you need to specify the DPM server name and a user name for a new local account to be created.
SetDPMServer.exe -DPMServerName <DPMServerName> -IsNonDomainServer -UserName <NewUserName>
You will be prompted to give a password for the new user account and to confirm it, once done the agent is configured and the relevant changes have been made to the Windows firewall.
3. Now the agent needs to be attached to the DPM server. Attaching DPM agents to a DPM server can be done through the DPM GUI .
- To attach a non-domain server agent:
- Open the DPM console
- Select the Management Pane
- on the Actions menu, Click Install
- Select Attach agents, when the Protection Agent Installation Wizard opens.
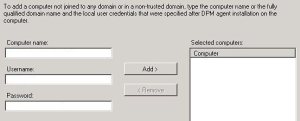
- Type the name of the untrusted computer that the DPM agent is installed on
- Type the user name and password specified when running SetDPMServer.exe.
- Click "Add >" to add the computer to the selected computers list.
- Click Attach
Now, you can create a protection group to protect the data on the machine. To do that, click on Protection Pane and select Create Proection Group, as usual
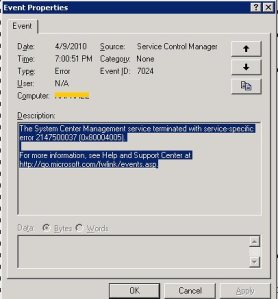
SCOM 2007 R2 : The System Center Management service terminated with service-specific error 2147500037 (0x80004005).
incorrect or create a new String Value (Reg_SZ) if missing and set it to the correct path
Desktop Virtualization Roadshow : Microsoft and Citrix are coming to Brisbane and Camberra, Australia
Learn how server & desktop virtualization can help you:
- Build a desktop virtualization management strategy that helps you manage your applications, data, mobile workers and multiple physical and virtual form factors.
- Reduce desktop costs.
- Enable flexible and agile IT through virtualization.
- Increase desktop security and compliance.
- Improve business continuity and end user productivity.
- Understand how Microsoft is building a solid foundation for a private cloud.
- Increase end user productivity and streamline your IT management with Windows 7.
| Apr 29 | Australia | Brisbane |  |
| May 6 | Australia | Canberra |  |
Register today!
VMware to create patch to fix performance behind Hyper-V R2 and XenServer
In a recent update of the phase II of Project VRC, VMware was behind Hyper-V R2 and XenServer.
Although XenServer and Hyper-V R2 performed nearly identical, Vmware get behind by 10%-30%. VMware responded to the findings and wrote a fix for VMware vSphere 4.0 to try to close the gap :
"…What we discovered led us to create a vSphere patch that would allow users to improve performance in some benchmarking environments."
There are three specific conditions that can excite this condition:
- A Xeon 5500 series processor is present with Hyper-Threading enabled,
- CPU utilization is near saturation, and
- A roughly one-to-one mapping between vCPUs and logical processors.
In this scenario, VMware vSphere favors fairness over throughput and sometimes pauses one vCPU to dedicate a whole core to another vCPU, eliminating gains provided by Hyper-Threading
VIRTUALIZING Terminal Server : analyzing Terminal Services (TS) workloads running on the latest generation hardware and hypervisors
Virtualizing Terminal Server and Citrix XenApp workloads is highly recommended, for managment and consolidation benefits and if you are thinking on x86 TS so far for more scalability.
So, If you are planning to run Terminal Server in a Virtual Environment, you shoud read the The Project VRC phase 2 whitepaper, that focuses completely on analyzing Terminal Services (TS) workloads running on the latest generation hardware and hypervisors.
Here is a brief summary :
"When comparing hypervisors, performance is close to equal throughout when no Hyper-threading is used by the VM’s. In all test the hypervisors perform with a 5% range with the Terminal Server workloads, with a slight edge for vSphere 4.0. Utilizing Hyper-Threading, on all platforms a performance increase in seen, but vSphere 4.0 trailing slightly by 15% in comparison to XenServer 5.5 and Hyper-V 2.0. These differences are only visible under full load.
Strikingly, XenServer 5.5 and Hyper-V 2.0 perform almost identical in all tests. The only differentiator between these two is that XenServer 5.5 (and vSphere 4.0) support 8vCPU’s, where Hyper-V 2.0 has a maximum of 4vCPU per VM"
if you are curious about the impact of different hypervisors and the performance differences with various hardware and if you are searching for best practices for your virtual Desktops … Project VRC whitepapers are a must read!
Dynamic Memory Coming to Hyper-V
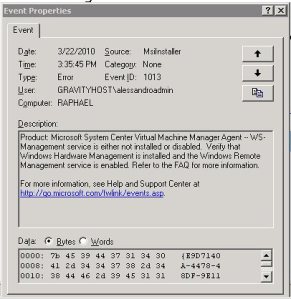
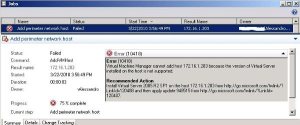
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager Agent — WS-Management service is either not installed or disabled.
"Product: Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager Agent — WS-Management service is either not installed or disabled. Verify that Windows Hardware Management is installed and the Windows Remote Management service is enabled. Refer to the FAQ for more information." 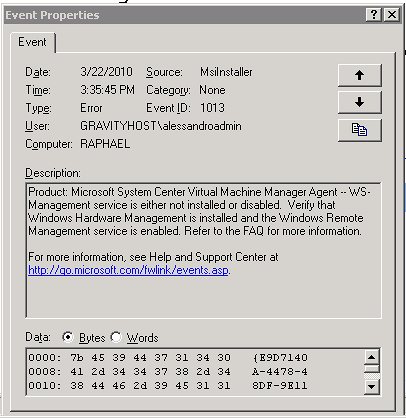
You should install the KB 936059. This update adds a new feature to Windows Remote Management (WinRM). This update also updates the version of Windows Remote Management that is included with Windows Server 2003 R2
Post-installation instructions
On a Windows Server 2003 R2-based computer that has the Windows Hardware Management optional component installed, the WsmanSelRg collector-initiated subscription collects events form the BMC. This subscription has a URI property that is set to wsman:microsoft/logrecord/sel. After you apply this hotfix, the WsmanSelRg subscription will not work until you set the URI property to the following:
To set the URI property, run the following command at a command prompt:
wecutil ss WsmanSelRg /uri:"http://schemas.microsoft.com/wbem/wsman/1/logrecord/sel
Windows 2008 R2 : No Restrictions for Network adapter teaming in cluster environment
In Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, there are no restrictions that are associated with NIC Teaming and the Failover Clustering feature and allows it to be used on any network interface in a Failover Cluster.
The following table details the recommended, supported, and not recommended network configurations for live migration, and is organized in the order in which each network configuration is commonly used. Before reviewing the table, note the following:
- When a network adapter is connected to a virtual switch, it is referred to as a virtual network adapter.
- Network access for virtual machines can be on either a public or private network. To allow virtual machines access to computers on the physical network, they must be on a public network. The requirements for virtual machine access vary depending on network I/O needs and the number of virtual machines you are running on a single physical server.
- In addition to the preferred network for the cluster and the Cluster Shared Volumes, a cluster can utilize at least one additional network for communication. This increases the high availability of the cluster. The cluster should also be on a private network.
- If a network configuration is listed as “not recommended” in the following table, it should not be used because the performance of live migrations declines and cluster nodes might crash. Add another network adapter to separate traffic between live migration and Cluster Shared Volumes.
| Host configuration | Virtual machine access | Management | Cluster and Cluster Shared Volumes | Live migration | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4 network adapters with 1 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 |
Network adapter 2 |
Network adapter 3 |
Network adapter 4 |
Recommended |
|
3 network adapters with 1 Gbps; 2 adapters are teamed for link aggregation (private) |
Virtual network adapter 1 |
Virtual network adapter 1 with bandwidth capped at 10% |
Network adapter 2 (teamed) |
Network adapter 2 with bandwidth capped at 40% (teamed) |
Supported |
|
3 network adapters with 1 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 |
Virtual network adapter 1 with bandwidth capped at 10% |
Network adapter 2 |
Network adapter 3 |
Supported |
|
2 network adapters with 10 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 |
Virtual network adapter 1 with bandwidth capped at 1% |
Network adapter 2 |
Network adapter 2 with bandwidth capped at 50% |
Supported* |
|
2 network adapters with 10 Gbps; 1 network adapter with 1 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 (10 Gbps) |
Network adapter 2 (1 Gbps) |
Network adapter 3 (10 Gbps) |
Network adapter 2 with bandwidth capped at 50% |
Supported |
|
2 network adapters with 10 Gbps; 2 network adapters with 1 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 (10 Gbps) |
Network adapter 2 (1 Gbps) |
Network adapter 3 (1 Gbps) |
Network adapter 4 (10 Gbps) |
Supported |
|
3 network adapters with 1 Gbps; 2 adapters are teamed for link aggregation (public) |
Virtual network adapter 1 |
Virtual network adapter 1 with bandwidth capped at 5% |
Network adapter 2 (teamed) |
Network adapter 2 with bandwidth capped at 90% (teamed) |
Not recommended |
|
2 network adapters with 1 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 |
Virtual network adapter 1 with bandwidth capped at 10% |
Network adapter 2 |
Network adapter 2 with bandwidth capped at 90% |
Not recommended |
|
1 network adapter with 10 Gbps; 1 network adapter with 1 Gbps |
Virtual network adapter 1 (10 Gbps) |
Virtual network adapter 1 with bandwidth capped at 10% |
Network adapter 2 (1 Gbps) |
Network adapter 2 with bandwidth capped at 90% |
Not recommended |
*This configuration is considered recommended if your configuration has a redundant network path available for Cluster and Cluster Shared Volumes communication.